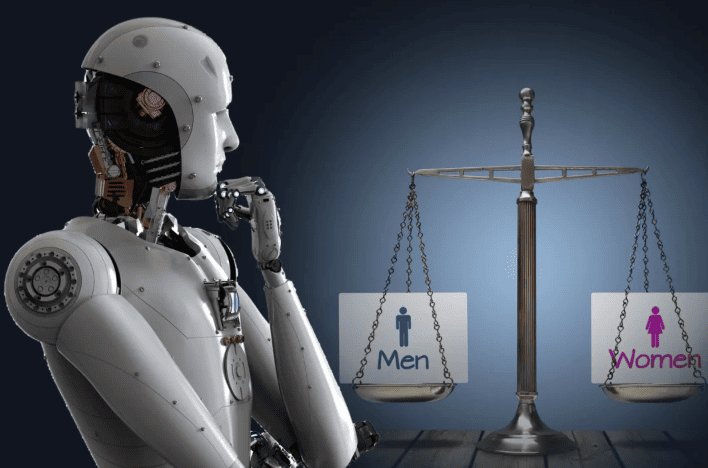
What is AI Bias? Examples, Types, and How to Prevent It
Every day, technology makes some big decisions about what programs we watch, which job applications are to be fast-tracked, or how schools review student performance. We generally believe that it's all neutral and fair because, well, it's a robot! And a robot does not have feelings. Yet sometimes, the fallout appears strange. A certain group might feel left out, or the outcomes just do not make sense.
That's what we call AI bias. Such biases can affect children's learning, restrict the jobs that people can get, and determine the information that individuals see on the Internet. So how does this happen? And more importantly, how do we stop a clever robot from unintentionally making life harder for some people?
What is AI Bias?
AI bias is when an artificial intelligence system gives results that are unfair, either in favor of or against an individual or group of individuals. This usually happens when the system is learning from data that is supposed to reflect existing human prejudices. In other words, if the world itself has biases, the AI will pick them up and sometimes even amplify them.

Bias in artificial intelligence could have far-reaching implications. Prejudiced systems could provide unjust results that would impact how our kids see the world. Let's look at some of the types of AI bias and real-world examples.
Types of AI Bias
AI bias is many-headed, and all tied to the data, the systems, and the people behind them. Understanding these types is the first step to recognizing how bias plays out in real-world applications.
- Racial bias occurs when systems reflect and perpetuate negative opinions toward any ethnic or cultural group. This is most often due to underrepresentation or misrepresentation in the data used for training.
- Gender bias is observed when an algorithm prefers one gender over another. It happens when a system magnifies existing social stereotypes or creates an echo chamber effect that does not welcome other points of view.
- Socioeconomic bias is the tilting of algorithms toward the preferences or behaviors of high-income groups, making access and fairness for lower-income individuals inconsistent.
- Age bias comes about when there's different treatment between older and younger people. One group gets priority in getting a job, health care, or financial services.
- Education bias happens when AI presumes to measure an individual's value or ability based on their level of formal education. It works against those with nontraditional paths.
Examples of AI Bias in Real Life
Here are a few examples of when people experienced AI in real life.
Stanford Facial Recognition (2023)

Scenario: Facial recognition technology is used to identify individuals for security and law enforcement purposes.
Bias: It is observed that algorithms do not as accurately recognize Asian and African-American faces. In fact, it is among African-American women that most misidentifications occur. The AI was trained on datasets where lighter-skinned faces were more heavily represented.
Result: A misidentification can lead to a false arrest, or someone being wrongly suspected, or unequal treatment by law enforcement.
Takeaway: Without careful oversight and diverse datasets, such technologies are enabled to perpetuate inequalities based on race and gender. This is a serious ethical and social issue.
Gender Bias in AI-Generated Images (2023)
Scenario: AI-generated pictures to represent workers in STEM fields
Bias: 75% to 100% show men in STEM fields. This reveals the belief that jobs in STEM are mostly for men. The AI learns from past data, which often shows more male experts than female ones. Even when women have the same skills, the AI keeps showing the old view that men are the main workers in these areas.
Result: This visual bias strengthens the notion that men dominate STEM fields, thereby potentially discouraging women from applying for positions related to engineering, science, or mathematics and sustaining gender gaps in these areas.
Takeaway: In the absence of vigilant supervision, varied viewpoints during creation, and continuous assessment, AI systems might inadvertently reinforce stereotypes rather than advocate for fairness.
UK A-Level Algorithm (2020)

Scenario: The United Kingdom employed an algorithm for grading A-Level exams because in-person testing was canceled due to the pandemic.
Bias: The algorithm based its decision predominantly on the historical performances of schools. Schools from low-income areas were more significantly penalized since their students scored lower in the past. The fact that students who had studied well and performed impressively did not matter.
Result: Grades were lower than what the hardworking students actually deserved, thus impacting their university intakes and futures.
Takeaway: This describes algorithmic bias whereby dependence on previous data highlights standing inequities instead of giving fair assessments to students. Human oversight is a component of fairness when making decisions that affect the future of individuals.
Simple Ways to Spot and Reduce AI Bias in Everyday Life
AI systems can sometimes treat people differently — and spotting those unfair patterns early helps protect your children and family. You don't need technical skills: these 4 simple habits will help you notice bias and act on it.
1 Question: Is This Fair for Everyone?
Whenever an app or tool makes a decision, do not jump to accept the decision; consider if it is fair. Would a different-aged, sexed, or colored person get that result?
If the answer is no, then you have more research to do. For example, if a job search website always boasts higher-paying jobs to men, one could question: Are women given an equal shot at opportunities here?
2 Don't Just Focus on One-off Mistakes
One wrong result can be noise. But the same unfair outcome happening again and again likely signals bias. For example, if a certain type of photo is always labeled incorrectly for darker skin, that's a pattern worth reporting.
3 Just Do Some Simple Home Tests to Find Bias
Bias is quite often uncovered by simply changing one small detail. For example, when registering to use an application, we can try to modify the name, age, or zip code of a profile and observe the changes. If the results are varied drastically, it is a red flag. For example, you could create two identical profiles and just change the female one to a male name. If at that moment the opportunities list shrinks, then it is very clear that the system is biased.
4 Observe Who Is Favored or Not Given Attention
Keep an eye on the patterns of who is included and who is excluded. What kinds of people are being shown in the recommendations, and who is never shown? If, for instance, a tutoring app is always picking out students from top schools and not mentioning others, then you are able to see bias.
Protecting Kids from Hidden Online Risks
Artificial intelligence isn't only used in workplaces. It also shapes the content that children and teenagers may come across on the Internet. Biased algorithms may influence the kind of videos, or games, or what social posts appear in front of them, subtly reinforcing stereotypes, or exposing one to unsafe material. This risk is often hidden from parents who otherwise worry but do not know how to effectively monitor or guide their child's digital experience.

AirDroid Parental Control is the answer to your problems. With the help of this app, families get the tools to create an environment that is safer for online users and at the same time encourage the responsible use of the device. Its main features are:
- Real-time screen monitoring: Check and find out which apps and websites your children are using with their consent.
- Content blocking: Allow only appropriate content by blocking harmful and/or inappropriate content.
- Alerts and notifications: You will be alerted on your phone the moment explicit terms appear in chats or searches.
- Location monitoring: You can see where your kid is at all times without having to call them constantly.
AirDroid Parental Control does not spy on your kids but teams up with them. With their awareness and consent, it helps families build trust while keeping an eye on the digital world.
Think of it as a helpful sidekick that is guiding kids through apps, videos, and websites where AI can sometimes play favorites or show the wrong stuff. A little monitoring, some gentle guidance, and suddenly the online world feels a lot safer and a lot more positive for everyone.
Conclusion
Global tech leaders are working to lessen bias in AI. And one of their goals is to balance out the demographics of those working on AI. For instance, Intel is attempting to increase diversity in its technical roles. You can still try to optimize AI fairness even if completely bias-free AI models are not yet feasible. Keep your family away from AI bias with Airdroid Parental Control for that extra support.












Leave a Reply.