Remote Patch Management: A Definitive Guide for 2025 [With Software Tips]

- 1 : What is Remote Patch Management? (And Why It's Non-Negotiable)
- 2 : The Three Pillars: Understanding the Types of Patch Management
- 3 : How Remote Patch Management Software Streamlines the Process
- 4 : Choosing the Best Remote Patch Management Software for Your Business
- 5 : Best Practices for an Effective Remote Patch Management Policy
1What is Remote Patch Management? (And Why It's Non-Negotiable)
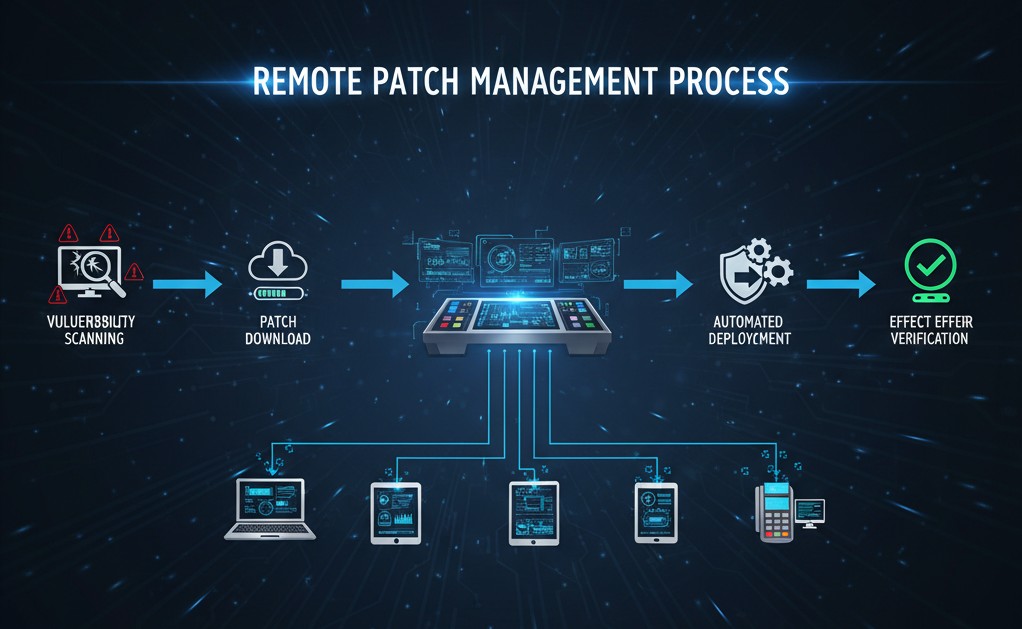
Let’s start by understanding what remote patching is and which core concepts define it.
Defining Remote Patching and Core Concepts
Remote patch management uses a centralized platform to manage the entire process of "vulnerability scanning → patch download → testing → automated deployment → effect verification" for devices (Windows/macOS/Linux terminals, IoT devices, Android POS machines, etc.) located in different regions and operating systems. Its core advantage over traditional manual patching lies in overcoming "geographical limitations" and "human efficiency bottlenecks"
For example, a chain retail company can use this model to achieve unified patch management for POS machines in 500 stores without requiring on-site IT personnel.
The Critical Importance of a Remote Patch Management Strategy

Why does remote patch management hold a key position within an enterprise’s security and risk management ecosystem? Let’s have a thorough view of how it is not just important but non-negotiable.
Security Protection: Blocking Vulnerability Attack Entry Points
2024 NVD (National Vulnerability Database) data shows that 76% of cyberattacks exploit "unpatched known vulnerabilities." Among ransomware attacks, 83% of victimized companies had "high-risk vulnerabilities unpatched for more than 72 hours." One medical clinic suffered losses exceeding 200,000 yuan due to a missed patch for the BlueKeep vulnerability in its Windows system, resulting in the locking of patient medical records. Hospitals using automated patching tools can reduce the time to patching high-risk vulnerabilities to within 2 hours.
Compliance Essentials: Avoiding Regulatory Penalties
HIPAA (Healthcare Industry) requires that "all medical device patch logs be retained for 7 years and traceable to the operator." PCI-DSS (Financial Industry) stipulates that "payment terminals must monitor patch status in real time, and the missed patch rate must not exceed 5%.”
One payment institution was fined 800,000 yuan by regulators for failing to retain POS machine patch logs. However, tools using compliance audit modules can automatically generate compliant reports, reducing audit preparation time from 2 weeks to 2 days.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency Improvement: Reduced Labor Costs
When manually patching devices, one IT staff member can only handle an average of 20 devices per day, and is prone to system crashes due to operational errors; automation tools can achieve "batch deployment + automatic rollback in case of anomalies," reducing the patch update time for 2000 devices from 3 days to 6 hours, and lowering labor costs by 70%.
2The Three Pillars: Understanding the Types of Patch Management
1. OS Patch Management
"Covering mainstream systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux, Windows devices, with an enterprise penetration rate exceeding 85%, have become the core scenario for patch management. This presents the dual challenges of 'full-type update coverage' and 'version fragmentation'
For example, enterprises may simultaneously have Windows 10, Windows 11, and older Windows Server versions, each with significantly different patch compatibility requirements.
Practical Recommendation: Group deployments based on 'device usage + business priority,' such as dividing devices into 'core server group' (databases, ERP systems, requiring priority patching), 'office terminal group' (patching can be done outside of working hours), and 'store POS machine group' (avoiding peak business hours 10:00-21:00). One manufacturing company reduced cross-system patch compatibility failures from 15 per month to 2 using this strategy."
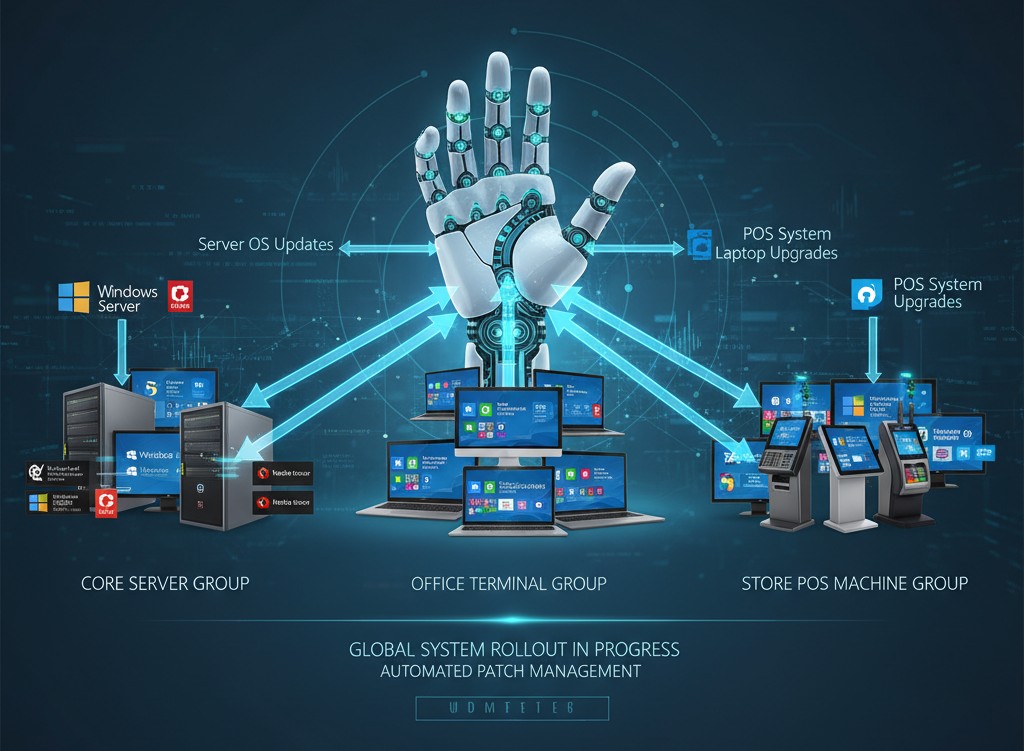
2. Third-Party Application Patch Management
Vulnerabilities in commonly used third-party software such as Adobe Reader, Chrome browser, Oracle database, and Java account for 45% of all enterprise vulnerabilities and are easily overlooked.
For example, a zero-day vulnerability in Chrome browser led to the compromise of employee email accounts in multiple companies. The core reason was that 'multiple Chrome versions (100/110/120) existed within the company, and manual patching could not cover all of them.'
Key functional requirements: The tool needs to support 'multi-version identification + unauthorized software blocking'—automatically scanning application versions on devices, pushing patches to older versions that do not meet security requirements, and simultaneously prohibiting the installation of unauthorized software (such as pirated Office). One law firm reduced the exposure of third-party software vulnerabilities by 90% using this function."

3. Enterprise-Specific Patch Management
"For industry-specific software, such as medical HIS systems, retail POS software, and logistics vehicle terminal systems, patches must balance 'functional stability' and 'peripheral compatibility.'
For example, when patching vehicle terminals for logistics companies, it's crucial to ensure uninterrupted GPS positioning and barcode scanner functionality; directly applying a general patching process might lead to data upload failures.
Key adaptation points: Choose tools that support 'business system integration testing'—before deploying patches, simulate compatibility with vehicle systems and barcode scanners in a sandbox environment to confirm no anomalies before pushing to the production environment. One logistics company reduced its patch-induced business interruption rate from 12% to 0.5% using this method."
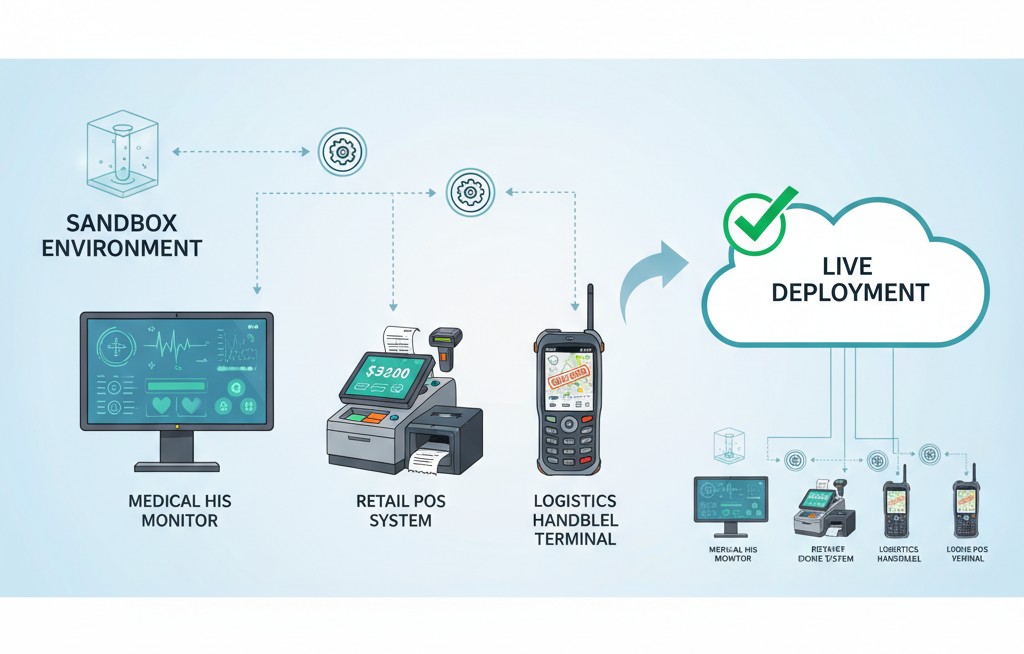
3How Remote Patch Management Software Streamlines the Process

Now that you know why enterprises can’t do without effective remote patch management and what are its various forms, let’s explore how a thoughtfully selected remote management software can streamline the entire process and how to make a wise decision while selecting one for your enterprise.
Key Features to Look For in a Remote Patch Solution
1. Intelligent Priority Engine: Sorting by "Risk + Business"
Patches are not necessarily "the more the better, the faster the better." They need to be dynamically adjusted based on "vulnerability risk level" and "business impact." For example, during major e-commerce promotions, "low-risk patches for non-core office terminals" can be delayed until after the promotion, prioritizing high-risk patches for the order and payment systems.
High-quality tools should support a three-dimensional sorting system based on "CVSS score (vulnerability risk) + EPSS exploitability score (probability of attack) + device business weight." One e-commerce platform used this feature to improve patch deployment efficiency by 3 times during a major promotion without affecting order processing speed.
2. Offline Patch Support: Solving Weak Network/Offline Device Issues
Field equipment (such as logistics tablets and on-site medical terminals) is often in a weak network or offline state, making it easy for general tools to experience "interrupted patch downloads or missed patches." Tools with an "offline patch queue" function can cache patches locally on the device and automatically resume downloads once the device is connected to the network. One food delivery platform used this function to increase the patch completion rate of its riders' tablets from 60% to 98%.
3. Compliance Audit Module:
Meeting Industry Traceability Needs. The tool must automatically record full-chain information such as "device number, patch version, deployment time, operator, success status, and reason for any anomalies," and support exporting reports according to standards such as "HIPAA/PCI-DSS/ISO 27001." For example, in the healthcare industry, logs can quickly pinpoint whether "a vulnerability patch on a specific diagnostic tablet was applied by an authorized doctor," avoiding liability disputes.
4. Anomaly Rollback Mechanism: Reducing Patch Failure Risk
Approximately 5% of patches may cause system crashes due to compatibility issues. High-quality tools should support "automatic anomaly detection + one-click rollback"—when a blue screen or unresponsive business system is detected, it automatically restores the system to its pre-patch state and pushes out an analysis of the cause of the failure. One financial institution used this feature to reduce patch failure handling time from 4 hours to 15 minutes, without causing business interruption for its clients.
4Choosing the Best Remote Patch Management Software for Your Business
Different types and sizes of businesses with different goals have different requirements for a patch management software. Below is a comprehensive guide on choosing the one that suits you the best.
Challenges of Manual Patching vs. Automated Software

Comparison Dimension | Manual Patching | Automated Tool (AirDroid Business) |
|---|---|---|
| Vulnerability Response Time | Windows devices: 72 hours; Android devices: 48 hours | Windows (high-risk): 4 hours; Android (high-risk): 90 minutes |
| Windows Patch Coverage | Can only handle security updates; 40% omission rate for other types | Full coverage (security / quality / drivers, etc.); 0% omission rate |
| Cross-System Support | Windows and Android require separate operations; low efficiency | Unified platform management; supports Windows 7–11 + Android 7–14 |
| Exception Handling | Requires manual investigation; average time 4 hours | Automatic repair + rollback; average time 15 minutes |
| Compliance Cost | Annual audit labor cost: $80,000+ | Automatically generates reports; annual cost approx. $5,000 |
Tool Positioning for Different Business Needs
The core of choosing a remote patch management tool is matching the enterprise's "equipment scale, system environment, and compliance requirements" because different types of enterprises have significantly different pain points, requiring targeted selection:
- (1) Small and medium-sized enterprises (mainly Windows devices, scale 100 units) Core Requirements: Lightweight operation, low cost, and low learning curve; quick and easy to use without complex configuration.
Compatible Tools: Prioritize tools that focus on "basic Windows patch functionality," supporting automatic scanning for Windows device vulnerabilities and one-click batch deployment of security updates. Free for up to 30 devices, suitable for small office scenarios (such as a design company with a 10-person team or a single retail store).
Important Notes: Avoid pursuing "full system coverage" to prevent increased maintenance costs due to redundant features; focus on meeting the basic requirement of "rapid Windows security patch repair." - (2) Medium and large enterprises (Windows devices account for ≥80%, scale ≥100 units, distributed across multiple departments/regions)
Core Needs: Efficient batch deployment, comprehensive Windows patch coverage, and visualized operations and maintenance, while reducing cross-departmental collaboration costs.
Recommended Tools: Solutions like AirDroid Business, which offer deep Windows optimization, are preferred. Their advantages precisely address the pain points of medium to large enterprises, supporting unified management of Windows devices across multiple regions nationwide (such as headquarters servers, branch office computers, and store POS terminals).
OTA batch deployment enables 'one operation for thousands of devices,' and provides a visualized dashboard for patch progress, eliminating the need for IT teams to check the status of each device individually.
Typical Scenario: A chain supermarket with 500 Windows POS terminals uses AirDroid Business's 'scheduled updates' feature to uniformly set patch deployment times to 2 AM (outside business hours) to avoid impacting customer payments, and the patch completion rate has increased from 75% with manual deployment to 99%." - (3) Compliance-sensitive industries (finance, healthcare, government affairs, Windows devices carrying core business)
Core Requirements: Compliance with official Microsoft patches, end-to-end audit logs, traceable vulnerability fixes, and compliance with regulatory inspections.
Suitable Tools: Tools that deliver official Microsoft patches and generate compliance reports (such as AirDroid Business or ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus) must be selected.
AirDroid Business's "Microsoft Official Patch" feature completely avoids the security risks of unofficial patches and automatically generates compliance reports including "missing patch list, failed update records, and device restart status," meeting the audit requirements for Windows device patches under the financial industry's PCI-DSS and the healthcare industry's HIPAA.
Case Study: A local bank used AirDroid Business to ensure 100% of patches for 200 Windows servers used official Microsoft packages. During audits, a PDF report containing "patch version, deployment time, and operator" can be directly exported, reducing audit preparation time from one week to one day."
AirDroid Business: Your Comprehensive Remote Patch Management Solution

Addressing the pain points of patch management for enterprises (especially those with a high proportion of Windows devices), AirDroid Business offers a closed-loop solution from vulnerability detection to remediation, centered on "end-to-end automation, full coverage of Windows scenarios, and compliance visualization." Key capabilities include:
- 1. Windows Patch Full-Scenario Coverage, No Omissions in Repair
Completely solves the problem of "multiple types of Windows patches and difficulty in management", supports 8 major categories of patches defined by Microsoft, and ensures comprehensive security of devices from system to application:
Security UpdatesEmergency repairs for Windows system vulnerabilities (such as BlueKeep, Log4j related vulnerabilities), automatic priority deployment, and the response time for high-risk vulnerabilities can be compressed to within 2 hours.
Quality UpdatesRepairs system stability issues (such as Windows 11 blue screen, file manager lag), no need for manual troubleshooting of the root cause of the fault, and automatic verification of function restoration after patch deployment;
Driver & Feature UpdatesAdapts to peripheral drivers such as printers and scanners, and synchronously supports the feature iteration of Windows 10/11 (such as taskbar optimization, multi-desktop enhancement), avoiding peripheral device shutdown due to driver incompatibility;
Microsoft Apps UpdateCovers security patches for Microsoft applications such as Office 365, Edge browser, and Teams, and solves The blind spot in security lies in the fact that "system patches have been applied, but application vulnerabilities still exist."
A manufacturing company used this feature to reduce the "patch miss rate" of its Windows devices from 18% to 0.5%, and experienced no security incidents due to Windows vulnerabilities throughout the year. - 2. Full-process automation reduces manual intervention by 90%.
From “vulnerability scanning” to “rebooting and finishing”, no manual intervention is required throughout the entire process, significantly reducing the IT team’s workload.
Automatic scanning and detection: Real-time monitoring of the patch status of Windows devices, completing a full network scan within 1 hour of a new patch release, generating a “list of devices that need repair”, avoiding omissions during manual inspection.
Intelligent classification and approval: Automatically classifying patches into “Critical,” “Important,” and “Optional” categories, supporting preset approval rules (such as automatically approving high-risk patches and requiring manual confirmation for optional patches).
One internet company reduced manual approval operations by 50+ times per month using this rule.
OTA batch deployment and reboot management: Supports cross-network (WiFi/4G/dedicated line) OTA batch installation, with the ability to set “batch deployment” (such as deploying 30% of devices first to verify compatibility), and also provides a “reboot scheduling” function.
Allowing restart times to be delayed until employees leave work, or staggered restarts by department, one company used this feature to reduce business interruption caused by restarts from 4 hours to 15 minutes.
Patch history tracking: Automatically retains patch records for all Windows devices (including deployment time, version, status, and operator), supporting searches by "device number, time range, and patch type," facilitating the tracing of the root cause of problems. - 3. Compliance assurance and visualization
Easily coping with regulation and operation and maintenance solves the pain points of "difficulty in proving patch compliance and difficulty in monitoring operation status", and provide practical compliance and management tools.
Microsoft official patch delivery: All Windows patches are directly sourced from Microsoft's official channels, without third-party modifications, eliminating "system anomalies caused by unofficial patches", while meeting the audit requirements of enterprises for "patent source compliance".
Visualized reports and dashboards: Display core data through an intuitive interface - "number of devices with missing patches, number of devices waiting to be restarted, analysis of reasons for failed updates, and progress of high-risk patch repair", allowing IT managers to grasp the status of the entire network in real time without manually summarizing in Excel;
Targeted problem repair: Provide solutions to typical problems in Windows patch management.
Forced update for stalled devices: Automatically identify patch stalls caused by "long-term user delays" and "continuous device startup", remotely trigger forced installation, and prevent devices from becoming security vulnerabilities due to "long-term lack of updates";
Rapid anomaly repair: For Windows In the event of a sudden system error (such as a system failing to boot due to an update failure or a blue screen caused by driver conflicts), the system can quickly deploy official Microsoft patches. One customer service center used this feature to reduce Windows device failure recovery time from 8 hours to 30 minutes.
The "Simplified Batch Operations" feature supports deploying the same patch to hundreds of Windows devices at once, automatically skipping "offline devices" and resuming the download automatically once the devices are online, avoiding repetitive manual operations. - 4. Practical Value: Making Windows Patch Management Safe, Efficient, and Worry-Free
A chain hotel group (300 stores, 800 Windows devices) achieved the following after using AirDroid Business:
Security: The rate of fixing high-risk Windows vulnerabilities increased from 72% to 100%, and there were no intrusions into guest room systems caused by Windows vulnerabilities throughout the year.
Efficiency: The IT team reduced the time spent on patch management per month from 40 hours to 4 hours, allowing them to focus on other core tasks.
Compliance: Successfully passed the information security audit of the tourism industry through Microsoft's official patch certification and visual reports, without any compliance penalties.
Whether it's the batch management of Windows devices in multiple regions or the strict requirements of compliance audits, AirDroid Business can provide a patch management solution that "does not require manual intervention," allowing enterprises to get rid of the dilemma of "missed patches, cumbersome deployment, and difficulty in proving compliance."
5Best Practices for an Effective Remote Patch Management Policy
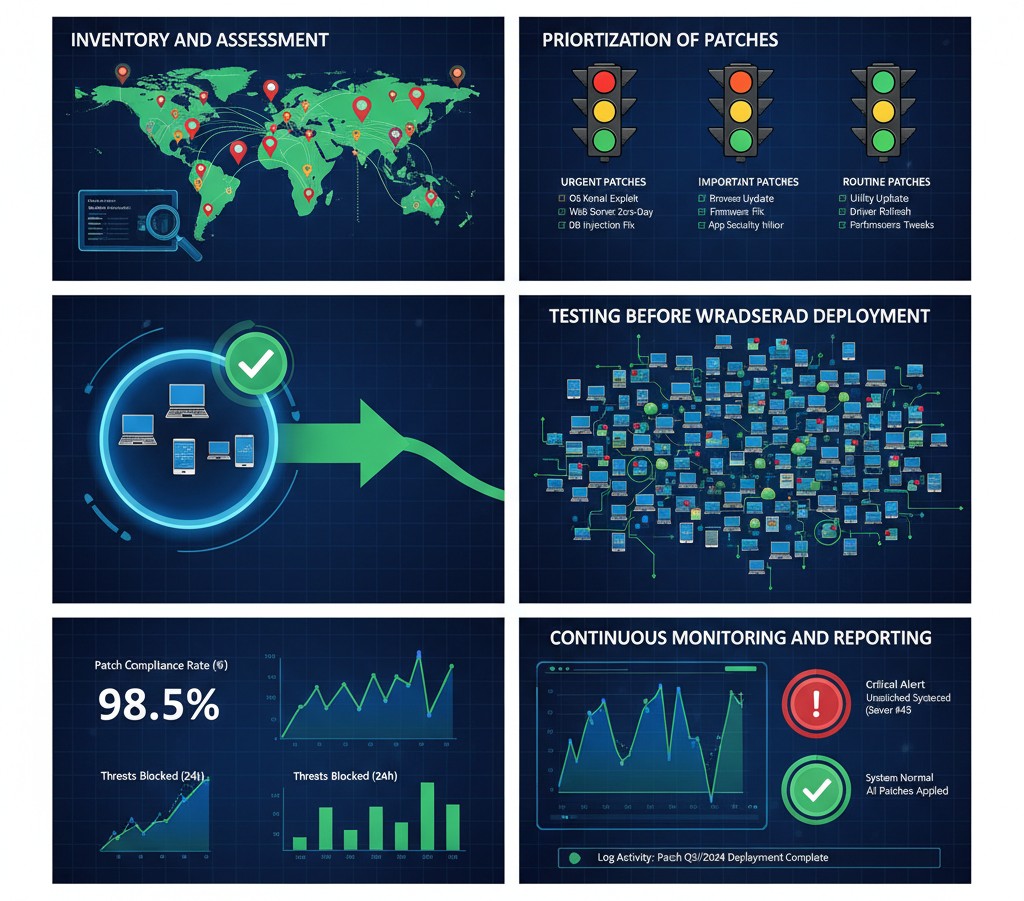
Inventory and Assessment
First, create a dynamic device list, labeling each device with its "department, location, system version, business purpose, and whether it is connected to the internet”, for example, "Beijing store POS machine (Android 9, for cashier use, weak network environment)" and "Shanghai headquarters database server (Linux, core business, dedicated network connection)."
One company missed patching high-risk vulnerabilities on 15 field tablets because it failed to label them as "offline devices." After implementing list management, the vulnerability patching rate dropped to 0.3%.
Prioritization of Patches
Prioritize into three levels based on 'risk impact + business needs,' focusing on core requirements for Windows devices:
Highest Priority: Security patches officially marked "Critical" by Microsoft (such as patches fixing remote code execution vulnerabilities), and driver/quality patches affecting core business operations (such as stability patches for POS machines and medical devices), must be deployed within 24 hours to mitigate attack risks.
Medium Priority: Non-core quality updates (such as general system bug fixes) and security patches for applications like Microsoft Office, which can be deployed in batches during off-peak hours (such as early morning).
Low Priority: Feature updates (such as system interface optimizations) and Defender definition updates, which can be merged into weekly/monthly patch windows to reduce device restart disruptions. Tools (such as AirDroid Business) can automatically prioritize based on 'Microsoft official categories + device business attributes,' eliminating the need for manual selection and improving efficiency."
Testing Before Widespread Deployment
- Sandbox Testing: Test patch compatibility with business systems in virtual machines consistent with the production environment—for example, test whether Windows patches affect ERP system operation, or whether Android patches cause POS machine scanning functionality to fail.
- Canary Deployment: First, push the patch to 20% of "non-core devices" (such as office computers in a certain area), monitor for 24 hours without any anomalies (such as blue screens or software crashes), and then deploy it fully. One retail company used this method to reduce patch-related POS machine failures from 12% to 0.8%.
Continuous Monitoring and Reporting
Monitor two core metrics through the tool dashboard:
- Patch Coverage: View patch omissions by "Device Group," such as "POS machine coverage in Beijing stores must be ≥99%";
- Compliance Rate: Compare with industry standards, such as "Patch log integrity rate for medical devices must be 100%." When an anomaly is detected (e.g., device coverage in a certain area is below 90%), an alert is automatically pushed and the cause is analyzed—if it's due to a weak network, "offline patch caching" is triggered; if it's due to patch conflicts, automatic rollback is initiated.
6Conclusion and Next Steps
The core of remote patch management is finding a balance between "security, compliance, and efficiency." Small and medium-sized enterprises can start with lightweight tools to control costs; medium and large enterprises, and enterprises with multiple systems/regions, are advised to choose full-featured platforms that support "cross-system + Android device adaptation" (such as AirDroid Business) to avoid repeated investment due to tool compatibility issues later; compliance-sensitive industries such as healthcare and finance should prioritize "audit capabilities" and "industry certifications."
Apply now for a 14-day free trial of AirDroid Business to experience unified patch management for Android devices and across systems; or download the "2025 Remote Patch Management Tool Selection Guide" to help you quickly find the right solution.







Leave a Reply.