- What Is an MDM Password Policy?
- What Are the Policy Requirements for a Password? Key Standards Explained
- MDM Password Policy for iPhone & Android: Key Differences
- What Is a Good Password Policy? Examples & Best Practices
- How to Create & Enforce an MDM Password Policy (With AirDroid Business)
- Compliance & End-User Guidance
1What Is an MDM Password Policy?

1What Is an MDM Password Policy? How It Fits into Basic MDM Policies
MDM password policies are a core component of mobile device management (MDM) solutions. They define the password rules that users must follow when accessing corporate mobile devices and data. These rules are designed to enforce strong password habits, thereby protecting sensitive information on devices from unauthorized access.
MDM password policies, in turn, are a key component of a broader MDM framework. MDM goes beyond managing devices to comprehensively manage the data, applications, and access permissions on devices. Password policies are the cornerstone of this framework, ensuring that only authenticated users can access managed devices and the corporate resources within them. They work in tandem with MDM features such as device encryption, application management, data loss prevention (DLP), and remote wipe to form an enterprise's mobile security defenses. For example, even if a device is lost, enforcing strong password policies can buy valuable time to protect data.
2Why Businesses Need an MDM Password Policy: 3 Core Benefits
Data security
This is the most immediate and crucial benefit. By enforcing complex passwords, regular password rotation, and lockout policies, MDM password policies significantly reduce the risk of data breaches caused by device loss, theft, or unauthorized access. They provide the first line of defense for sensitive business data, customer information, and proprietary data on devices.
Meeting compliance requirements
Many industry regulations and international standards have clear requirements for data protection and access control. For example, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and ISO 27001 all require companies to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect data. A strong MDM password policy is a key component of meeting these mandatory compliance requirements, helping companies avoid significant fines and legal disputes.
Improving overall security strategy
MDM password policies are a crucial component of an enterprise's IT security strategy. They help cultivate good employee security habits and reduce security vulnerabilities caused by weak or reused passwords. By standardizing and automating password management, companies can establish a stronger and more consistent defense against increasingly sophisticated and evolving cyber threats.
Still managing password policies manually? AirDroid Business helps you achieve security and compliance with ease!
Tired of manually updating passwords on hundreds of devices? With AirDroid Business's centralized management and automated deployment features, you can easily meet complex password policy requirements. Configure once, sync to all, and make data security a simple task.
2What Are the Policy Requirements for a Password? Key Standards Explained
Developing an effective MDM password policy requires compliance to industry best practices and relevant standards. Here are some key general and industry-specific requirements:
1Universal Password Policy Requirements (ISO/NIST Standards)
ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System)
As one of the most widely recognized international information security standards, ISO 27001 provides specific requirements for access control and password management in Annex A. It emphasizes that organizations should have clear password usage policies, including password complexity, uniqueness, minimum length, regular changes, and measures to protect passwords from disclosure.
NIST SP 800-63B Digital Identity Guidelines
This guideline, published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), provides authoritative recommendations for digital identity authentication and access control. Regarding passwords, NIST recommends focusing on both "memorability" (i.e., whether the user can remember it) and "strength" (i.e., whether the password can withstand brutal attacks).
Recommended password requirements include
- Minimum length: At least eight characters are generally recommended, but longer passwords (e.g., 12-14 characters) are more secure.
- Complexity: A combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters is generally recommended.
- No common, compromised, or guessable passwords:
Dictionary words, usernames, birthdays, or passwords known to have been compromised should be prohibited. - Password history: Reusing recently used passwords is prohibited.
- No mandatory password changes:
NIST's latest recommendations do not require users to change their passwords regularly unless there is evidence of a compromise. Instead, more emphasis should be placed on the strength of the initial password and detecting unusual login behavior.
2Industry-Specific Password Requirements (e.g., Healthcare, Finance)
In addition to the Common Standard, certain industries have stricter password policy requirements due to the sensitivity of the data they handle:
HIPAA (Healthcare)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) imposes strict regulations on the security and privacy of protected health information (PHI). Regarding passwords, HIPAA requires healthcare entities to implement access controls to ensure only authorized personnel have access to PHI. This includes enforcing the use of strong passwords, regularly reviewing access rights, and maintaining audit trails for all PHI access. Specifically, passwords must be at least 10 characters long and must contain special characters. Passwords must be updated every 60 days, and all password changes must be logged.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
For organizations that process, store, or transmit cardholder data, PCI DSS mandates strict password policies.
These include:
- changing default passwords for all system components
- enforcing complex passwords of at least seven characters containing both numbers and letters
- requiring employees to change their passwords every 90 days
- not allowing the reuse of the last four passwords
- locking user IDs after six consecutive failed attempts.
Public sectors (such as government agencies):
- Passwords must be updated every 45 days, with hardware support.
- Key (such as USB shield) is used as auxiliary verification
- Password modification is prohibited in unauthorized network environments.
3MDM Password Policy for iPhone & Android: Key Differences
Although MDM platforms can provide unified management, there are some inherent platform feature differences in the implementation of password policies on iOS and Android systems.
1MDM Password Policy for iPhone: iOS-Specific Rules
Apple maintains tight control over its ecosystem, so MDM password policies for iOS devices are typically more uniform and strict. MDM administrators can set the following key password policies for iPhones and iPads:
- Password type: MDM enforces the use of complex passwords or 4-6 digit PINs.
- Minimum password length: For example, it may require passwords to be at least 6 or 8 characters.
- Require complex characters:
MDM solution enforces passwords to contain at least three of the following: numbers, uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and special characters. - Maximum failed attempts: It defines the maximum number of failed password attempts allowed before the device is locked or wiped.
- Screen lock duration: It sets the duration of time after which the device automatically locks.
- Password expiration: MDM forces users to change their passwords after a specific time interval.
- Password history: It restricts users from reusing recently used passwords.
- Biometric integration: To enable Face ID/Touch ID as an alternative to a password, you must manually enable the permission in the MDM backend and require a "backup password" (to prevent unlocking if biometric authentication fails).
- Effective mechanism: After the new password policy is pushed, users will be prompted to update the policy the next time they unlock their device, and this cannot be skipped (iOS System-level restrictions).
- Device Wipe: After multiple consecutive passcode attempts, you can configure a remote wipe of device data to protect your information.
iOS MDM policies ensure that all managed devices meet high standards of security and consistency.
2MDM Password Policy for Android: Customization for Different Brands
Due to the openness and diversity of the Android ecosystem (different manufacturers, customized UIs, and Android versions), enforcing MDM password policies can be more challenging than iOS.
- General Rules: Pattern, PIN, and password are supported, but MDM can disable the less secure "pattern lock."
- Brand Features:
- Samsung Knox: Supports two-factor authentication ("encrypted password + fingerprint") and can set "auto lock when device is away" (triggered by proximity sensor).
- Stock Android: Devices like Pixel phones require manual password complexity configuration, and some older versions do not support "history password restrictions."
- Scope: MDM password policies may be ineffective on rooted Android devices, requiring pre-configured device rooting status detection and access restrictions within MDM.
The emergence of Android Enterprise has significantly standardized the management of Android devices, enabling MDM platforms to provide unified and robust password policy controls.
- Separate work and personal profiles: Set independent, stricter password policies for work profiles while maintaining more relaxed password requirements for personal profiles.
- Password quality requirements: For example, "Medium" or "High" passwords.
- Minimum length and complexity: Set a minimum password length and required character types.
- Maximum number of failed attempts and device wipe: Configure the number of failed attempts and remote wipe policies.
- Screen lock time: Set the automatic lock time after the device is idle for a specified duration.
- Password expiration and history: Force password changes and limit password history.
- Encryption requirements: Enforce full-disk encryption or work profile encryption on devices for enhanced data protection.
4What Is a Good Password Policy? Examples & Best Practices
A "good" password policy requires a delicate balance between security, usability, and compliance.
1 Example of a Basic Password Policy (Suitable for Small Businesses)
For small businesses with limited resources, a concise yet effective password policy template can serve as a starting point:
- Minimum password length: 8-10 characters.
- Password complexity: Must contain at least three of the following: uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Password expiration: Enforce password changes every 90 days.
- Password history: Disallow the reuse of the last five passwords.
- Device lock: Locks the device for 30 minutes after 5-10 incorrect attempts.
- Auto-screen lock: Automatically locks the screen after 15 minutes of inactivity.
- Suitable scenarios: Employees bring their own devices (BYOD) and data has low sensitivity (such as general administrative documents).
- Benefits: It balances security with user experience, reducing employee resistance.
2 Advanced Password Policy Example (Enterprise-Grade)
For large enterprises or organizations handling highly sensitive data, more stringent and granular policies are required:
- Minimum password length: 12-16 characters or longer, with a passphrase recommended.
- Password complexity: Enforce the inclusion of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and all special character types.
- Password expiration: Regular password changes (as recommended by the latest NIST recommendations) may be optional, but should be combined with:
- 1. High complexity requirements: Initial passwords must be extremely strong.
- 2. Anomalous behavior detection: Real-time monitoring and alerting for suspicious login activity (such as remote logins and forceful cracking attempts).
- 3. Compare passwords against a public database of compromised passwords and immediately force a password reset if an employee's password is found to be compromised.
- Password History: Reuse of the last 10-24 passwords is prohibited.
- Device Lock and Wipe: After 3-5 incorrect attempts, the device can be permanently locked or remotely wiped (depending on the sensitivity of the data).
- Auto-Screen Lock: The device automatically locks after 5 minutes of inactivity.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA is mandatory for accessing critical enterprise applications or data.
- Biometric Integration: Fingerprint/facial recognition is allowed as a secondary unlock method, but a strong password is still required in the background.
- Device Encryption: Full-disk encryption is mandatory for all devices.
- Useful Scenarios: Company-issued devices that store sensitive information such as customer data and financial statements.
- Benefits: Meets ISO 27001 compliance requirements and reduces risk through multi-factor authentication.
3 Best Practices
- Balance: Find the optimal balance between security and user convenience, avoiding overly restrictive policies that may lead to user resistance or avoidance.
- Tiered Management: Develop different levels of password policies based on employee roles and the sensitivity of the data they access.
- User Education: Provide ongoing cybersecurity awareness training to employees to ensure they understand the importance of password policies and learn how to create and manage strong passwords.
- Regular Review: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of password policies and adjust them based on the latest security threats and compliance requirements.
5How to Create & Enforce an MDM Password Policy (With AirDroid Business)
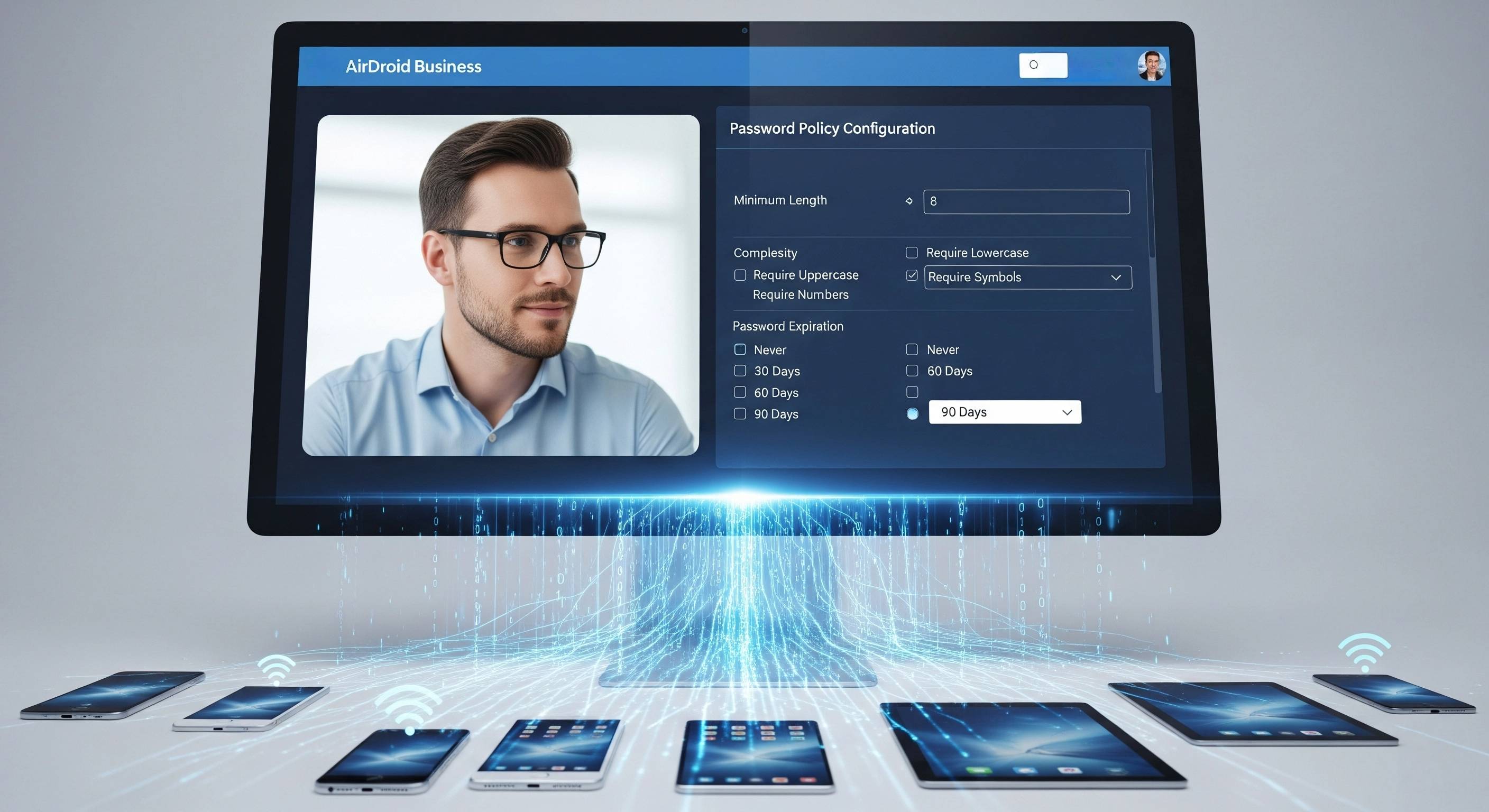
Creating and enforcing MDM password policies is typically accomplished through a dedicated MDM platform. Let’s use AirDroid Business as an example to outline the process for building and streamlining MDM password management.
1 3 Steps to Build Your MDM Password Policy
- Step 1: Needs Assessment and Planning:
- Clear Objectives: Determine the type of data and sensitivity to be protected.
- Identify User Groups: Differentiate between employees in different departments and roles, who may require different access rights and password strengths.
- Reference Standards: Based on your company's industry and region, reference relevant compliance standards (such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001) to determine a policy baseline.
- Estimate Impact: Consider the impact of new policies on user workflows and plan communication and training in advance.
- Step 2: Configure Policies in AirDroid Business:
- Log in to your AirDroid Business management console.
- Navigate to the "Policy & Kiosk" module.
- Create a New Policy Config file and select the "Password" option.
- Based on the plan from step 1, configure specific password requirements, such as:
- Minimum password length
- Password complexity (numbers, letters, and special characters)
- Password expiration time
- Password history limit
- Device lock attempts and lock duration
- Auto-screen lock time
- Remote wipe option
- Example: In the AirDroid Business interface, you'll see clear configuration options; simply check the required items and enter the parameters.
- Step 3: Deployment and Communication:
- Deploy policies: Push the configured password policy to target device groups or individual devices. AirDroid Business supports assigning policies to specific users, device groups, or all enterprise devices.
- Effective communication: Clearly explain the new password policy changes to all affected employees, the reasons for them, and how they need to comply. Provide user-friendly guides, FAQs, or even organize a brief training session. Emphasize that these policies are meant to protect company and employee personal information, not to create unnecessary friction.
For a more detailed tutorial, refer to this link: Password Policies Tutorial
2 How AirDroid Business Simplifies MDM Password Management
- Centralized Management: Through the single AirDroid Business management console, IT administrators can centrally configure and deploy password policies to all managed Android devices, regardless of brand or model.
- Automated Enforcement and Compliance Monitoring: Once policies are deployed, AirDroid Business automatically enforces them on devices. It also monitors the password compliance status of devices in real time, identifies devices that do not comply with policies, and provides detailed compliance reports for easy auditing and management.
- Powerful Security Controls: In addition to basic password policies, AirDroid Business supports advanced security features such as mandatory device encryption, remote lock, remote data wipe (in case of device loss or theft), and application whitelisting/blacklisting, providing multi-layered protection for corporate data.
- Remote Password Reset: If an employee forgets their password, IT administrators can remotely and securely reset their device password through AirDroid Business, reducing the need for manual intervention and improving efficiency.
- Flexible User Group Management: You can create different user groups based on department or device type and apply customized password policies to each group for granular management.
Get your MDM password policy done in three steps! Use AirDroid Business to make management simple and efficient
Is implementing MDM password policies too complicated? AirDroid Business offers an intuitive and easy-to-use management console. In just three steps, you can configure requirements for minimum length, complexity, expiration, and more, all while monitoring device compliance in real time. Focus on your business and let AirDroid Business handle device security.
6 Compliance & End-User Guidance

1 Mandatory Requirements from GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Requires companies to protect personal data through "appropriate technical and organizational measures." MDM password policies are key to implementing strong passwords, strict access controls, and data encryption.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): The HIPAA Security Rule explicitly requires access controls for ePHI. MDM password policies ensure only authorized personnel can access ePHI by enforcing complex passwords and authentication mechanisms.
- ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System): The "Access Control" section explicitly requires password management and user access management. MDM password policies help companies establish an ISO 27001-compliant information security management system.
Achieve both security and convenience. AirDroid Business provides a worry-free experience for you and your employees.
Worried that a strict password policy will impact the employee experience? AirDroid Business balances security and convenience. With the remote password reset feature, IT administrators can quickly help employees who forget their passwords, saving valuable time. Flexible user group management also ensures that employees in different departments have password policies that best suit their work environment.
2 End-User FAQs: Forgotten Passwords & Usability
End-User FAQs: Forgotten Passwords & Usability
- User Self-Reset: Use the self-reset feature provided by the MDM system (e.g., AirDroid Business's End-User Portal).
- IT Administrator Remote Reset: The administrator can log in to the MDM console to reset the password remotely.
- Strengthening user education: Conduct regular cybersecurity awareness training and communicate policy changes.
- Introducing multi-factor authentication (MFA): Use MFA methods like fingerprint and OTP tokens to improve security.
- Adopting an intelligent password policy: Prioritize password strength and uniqueness over frequent changes, and detect compromised passwords for resets.
- Providing convenient tools: Encourage the use of password managers and self-service portals for easy password management.
- Continuous review and adjustment: Regularly evaluate and optimize password policies based on new threats and user feedback.









Leave a Reply.