MDM (Mobile Device Management) Integration: Definition, Benefits & How to Implement
By integrating MDM, enterprises can enhance security, simplify IT operations, and support remote work environments while maintaining full control over devices. This is critical to addressing the growing threat of cybercrime. According to research by Cybersecurity Ventures, by 2025, the losses caused by cybercrime are expected to reach $8 trillion per year. MDM solutions play a key role in mitigating these risks, protecting sensitive data, and simplifying IT operations. Before we can delve into the steps involved, let’s get an understanding of what MDM integration is and how it is beneficial for enterprises.
1What is MDM Integration
MDM integration (mobile device management integration) refers to the process of connecting the MDM (mobile device management) system with other enterprise IT systems, applications or services (such as identity authentication platforms, ERP, CRM, cloud services, office software, etc.) through technical means, so that the systems can work together efficiently and data can flow in real time.
MDM integration (mobile device management integration) refers to the process of connecting the MDM (mobile device management) system with other enterprise IT systems, applications or services (such as identity authentication platforms, ERP, CRM, cloud services, office software, etc.) through technical means, so that the systems can work together efficiently and data can flow in real time.MDM integration (mobile device management integration) refers to the process of connecting the MDM (mobile device management) system with other enterprise IT systems, applications or services (such as identity authentication platforms, ERP, CRM, cloud services, office software, etc.) through technical means, so that the systems can work together efficiently and data can flow in real time.
In simple terms, the MDM is a tool for managing mobile devices, and "integration" is to allow this tool to break through the limitations of "single device management" and integrate into the overall IT ecosystem of the enterprise, becoming a bridge connecting devices, users, and businesses.
In simple terms, the MDM is a tool for managing mobile devices, and "integration" is to allow this tool to break through the limitations of "single device management" and integrate into the overall IT ecosystem of the enterprise, becoming a bridge connecting devices, users, and businesses.In simple terms, the MDM is a tool for managing mobile devices, and "integration" is to allow this tool to break through the limitations of "single device management" and integrate into the overall IT ecosystem of the enterprise, becoming a bridge connecting devices, users, and businesses.
2MDM Integration Styles and Technologies
There are typically four ways in which MDM integration for enterprises can be attained, each one with its own benefits and limitations. Let’s explore them one by one
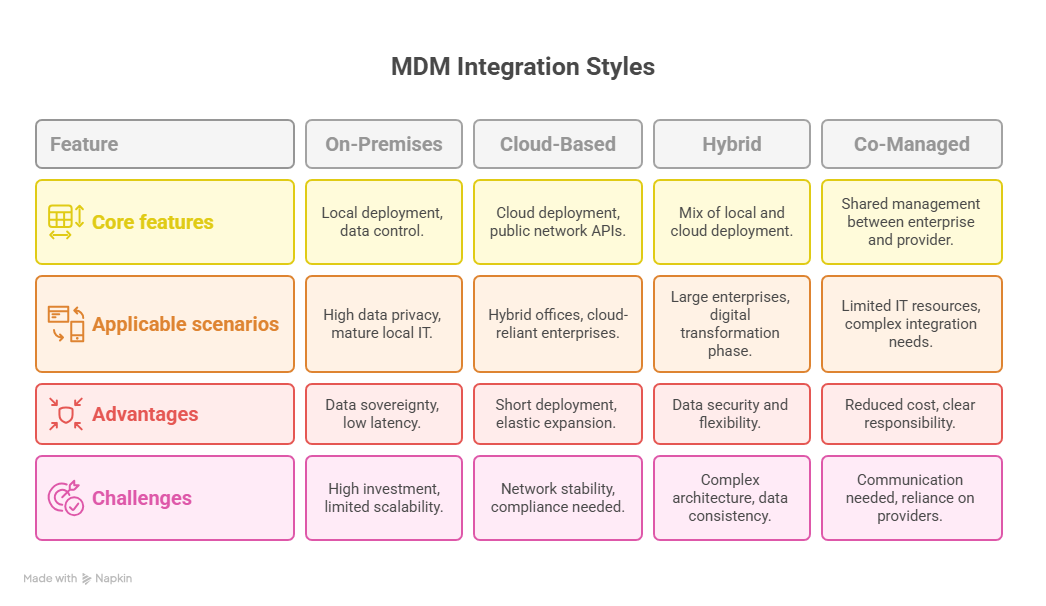
Four Main Styles of MDM Integration
Below is a detailed account of the four most common MDM integration styles along with their Features, applicable scenarios, advantages, and disadvantages.
On-Premises Integration
Core features:
The MDM server and the system to be integrated are deployed in the enterprise's own data center, and data interaction is achieved through the local network (LAN/WAN) or internal API. Data storage and processing are completed entirely within the enterprise.
Applicable scenarios:
Industries with extremely high requirements for data privacy and security (such as finance, medical care, and government) need to strictly control data outbound.
There is a mature local IT architecture, and the system is difficult to migrate to the cloud, such as old industrial control systems.
Advantages:
Data sovereignty is completely controlled by the enterprise, with low latency, suitable for highly sensitive data interaction.
Challenges:
Large initial hardware investment, dedicated personnel are required to maintain the server, and scalability is limited by local resources.”
Cloud-Based Integration
Core features:
MDM systems (such as Air Droid Business cloud version) and integration objects (such as Azure AD, in tune, SaaS applications) are deployed in the cloud, and linkage is achieved through public network APIs, standardized protocols (such as OAuth 2.0, SAML) or third-party cloud integration platforms (such as Zapier). Data flows in the cloud through encrypted channels.
Applicable scenarios:
Enterprises that use hybrid offices or global teams require cross-regional access management.
Light-asset enterprises that rely on cloud services (such as Microsoft 365, Salesforce);
Small and medium-sized enterprises that want to deploy quickly and reduce local operation and maintenance costs.
Advantages:
No need to build servers by yourself, short deployment cycle (usually completed within a few days), and elastic expansion as the business grows.
Challenges:
High reliance on network stability and the need to ensure the compliance of cloud service providers (such as GDPR, ISO 27001)."
Hybrid Integration
Core features:
Combining the advantages of local deployment and cloud integration, some systems (such as core business databases) retain local deployment, and other parts (such as mobile office applications) use cloud integration, and achieve cross-environment data synchronization through "local gateway + Cloud Bridge".
Applicable scenarios:
Large enterprises have multiple business lines coexisting, some systems need local control (such as production systems), and some need flexible cloud expansion (such as remote office tools);
In the transition period of digital transformation, it is impossible to migrate all systems to the cloud at once.
Advantages:
Taking into account data security and flexibility, integration can be promoted in stages to reduce transformation risks.
Challenges:
The architecture is relatively complex, and it is necessary to coordinate local and cloud permission management and data consistency, such as avoiding information deviation caused by synchronization delays.
Co-Managed Integration
Core features:
Integration is completed by the enterprise IT team and the MDM service provider (or third-party integration service provider) through division of labor and collaboration: the enterprise is responsible for the permission opening and demand definition of the core system, and the service provider is responsible for technical implementation. Both parties share the management console or collaborate on operation and maintenance through permission division.
Applicable scenarios:
The enterprise IT team has limited resources and lacks professional integration developers.
The integration requirements are complex (such as cross-industry system docking, such as the POS system + logistics tracking system in the retail industry).
Scenarios where you want to implement quickly but need to retain core control.
Advantages:
Reduce the cost of self-research by the enterprise, use the experience of the service provider to avoid technical pitfalls (such as API version compatibility issues), and have clear responsibility boundaries.
Challenges:
It is necessary to establish an efficient communication mechanism to avoid deviations in demand transmission; long-term reliance on service providers may lead to increased operation and maintenance costs.
Now that you know the four types of MDM integrations, the question is, how to select the most suited option for yourself? Here is the main criterion you should prioritize:
- Prioritize data sensitivity:
- Evaluate IT team resources:
- Combined with business scalability:
If the core data needs to be controlled locally, go for the local/hybrid mode. However, for non-sensitive data, cloud mode can be relied upon.
If you lack technical personnel, we would suggest going for a collaborative management mode. However, if you have a mature team, you can choose local/cloud independently.
If you are looking forward to rapid expansion or globalization, prioritize cloud/hybrid mode, but for stable architecture, local mode is more controllable.
The advantage of Air Droid Business is that no matter which mode is chosen, it provides standardized integration tools (such as open APIs, pre-configured templates) and customized services to help enterprises reduce the cost of mode switching and achieve "one-time deployment, multi-scenario adaptation."
Common Systems and Technical Paths for MDM Integration
Common Integration Technologies and APIs
There are typically three integration technologies used for the process of MDM integration. Let’s have a brief introduction to each one of them.
1. RESTful APIs
Role: RESTful API follows the principles of client-server architecture, stateless communication, and unified interface, making it an ideal choice for connecting different IoT devices and services. They provide semantic CRUD operations through HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, making APIs intuitive and easy to discover.
Air Droid Business App: Provides remote control APIs that can be integrated into ITSM, CRM, and other systems to shorten problem-solving time and improve efficiency.
Value: it helps in real-time data interaction, turning MDM from a static tool into a dynamic response center, hence ensuring quick decision making.
2. Webhooks
Function: Webhooks are user-defined HTTP callbacks that enable real-time, event-driven communication. They are triggered by specific events or conditions (e.g., sensor thresholds exceeded), eliminating the need for continuous polling, reducing network traffic and latency.
MDM application scenarios: When the device status changes (e.g., jailbroken, offline), SIEM alerts or ITSM work order creation are automatically triggered to ensure information synchronization.
Value: Build an active early warning system, allowing MDM to move from passive recording to active response, and help real-time threat detection.
3. SDK (Software Development Kit)
Purpose: SDKs provide a set of tools, libraries, documentation, and sample code to help developers build applications that integrate with MDM solutions. They simplify the process of interacting with MDM platforms. For example, the Salesforce Mobile SDK supports the configuration, update, and authentication of connected applications using MDM.
MDM use cases: MDM SDKs can be used to develop custom applications to interact with the MDM Hub in real time. For example, Informatica MDM's SIF SDK allows developers to build Java applications and web services that communicate with the MDM Hub. Android Enterprise provides APIs to manage device deployment, such as enforcing password requirements or remotely installing applications.
Value: Enable enterprises to customize integration, adapt MDM to specific business needs, and upgrade from a general tool to a dedicated solution.
4. Directory services (such as Azure AD, LDAP):
Role: Integration of MDM with directory services is essential for device registration, user authentication, and access control. It allows MDM solutions to leverage existing user identities and group information to manage devices and policies.
MDM use cases: Integrate with Azure AD to enable automatic device registration and single sign-on, and synchronize user group information through LDAP to assign device policies.
Value: Build a unified identity management system, simplify permission allocation, and improve the level of refined security management and control."
Common Systems for MDM Integration
1. Integration with Identity and Directory Services (e.g., Azure AD, LDAP)
Core value: synchronize user information to achieve full life cycle rights management; automatically match device policies based on user groups; support single sign-on to improve user experience.
Typical scenarios
- 1. A manufacturing company uses LDAP to store employee directories. After MDM is integrated with it: when new employees join the company, LDAP automatically pushes user information to MDM, and the device automatically joins the "device group of the department" after activation; when employees transfer positions, the directory service updates the user group, and MDM adjusts the device permissions synchronously (such as switching from "production workshop group" to "quality inspection group", and the device automatically disables access to the production system).
- 2. Multinational companies use Azure AD to achieve global user management. After MDM is integrated with it, the devices of employees in the Asia-Pacific region can only access cloud resources in the region to avoid cross-border permissions.
2. Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and IT Service Management (ITSM) Tools
Core Value: SIEM integrates device events and identifies potential threats; ITSM automatically creates equipment failure tickets to speed up problem solving and form a closed loop of security and operation.
Typical scenarios
- 1. After a financial enterprise's SIEM platform integrates MDM: When it detects that the same device attempts to access sensitive databases multiple times within 1 hour, and the MDM log shows that the device was jailbroken 3 days ago, SIEM automatically triggers a high-risk alarm and remotely locks the device through MDM;
- 2. Retail chain brands integrate ITSM with MDM: When a store's POS device is offline for more than 10 minutes, MDM automatically creates a ticket to ServiceNow and assigns it to a regional IT engineer. The ticket includes the device location and network diagnostic log. Engineers can remotely troubleshoot problems through MDM, increasing repair efficiency by 60%."
3. Integration with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Human Resources (HR) Systems
Core value: ERP synchronizes equipment cost data for accounting, and restricts equipment access scope in reverse; HR system triggers employee resignation process, and MDM automatically performs data erasure and equipment lock.
Typical scenarios
- 1. After a retail enterprise's ERP system is integrated with MDM: the monthly traffic fee and maintenance cost of each store's equipment are automatically counted and allocated to the store performance report; at the same time, the "product promotion activity" data of ERP is synchronized to MDM, and the store equipment automatically pushes the corresponding promotion posters without manual operation.
- 2. The HR system of a group enterprise is linked with MDM: After an employee submits a resignation application, the HR system notifies MDM 24 hours before the "last working day". MDM first freezes the internal communication function of the device. After the employee completes the formalities, the data is erased with one click, and the device is marked as "to be recycled" to avoid data leakage risks."
3Choosing the Right MDM Integration Solution: AirDroid Business
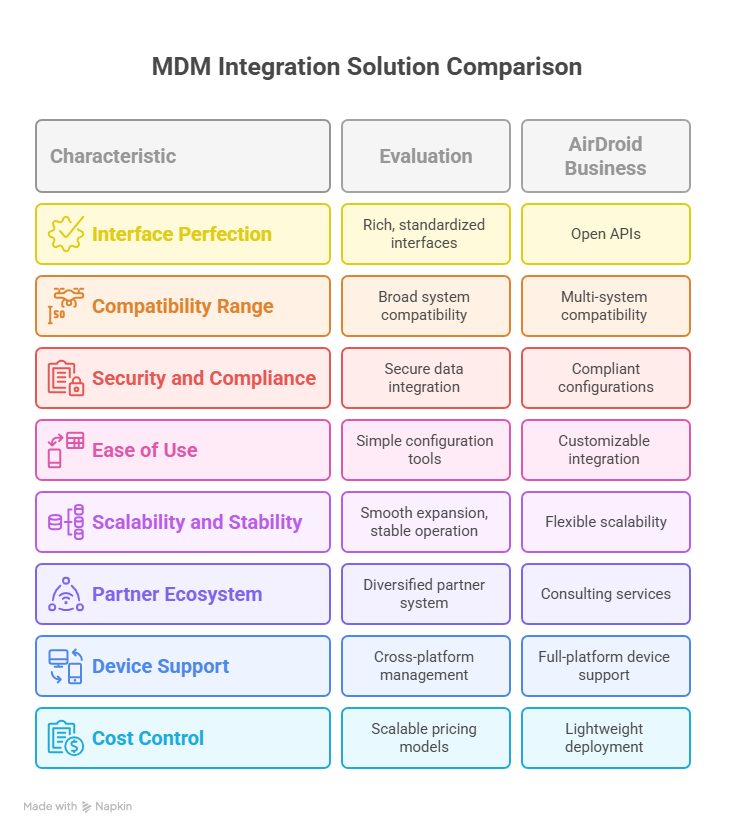
How to Evaluate the Integration Capabilities of MDM Solutions
To evaluate the integration capability of an MDM solution, you need to focus on the following key points to ensure that it can meet the actual needs of the enterprise:
Interface and ecological perfection
Check whether it has rich and standardized interfaces (such as RESTful API, Webhooks, etc.), whether the interface documentation is detailed, and whether it provides development tools such as SDK. At the same time, understand its compatibility with mainstream systems (such as Azure AD, SAP, ServiceNow, etc.) and whether there are mature integration cases.
Compatibility range
Confirm whether the solution is compatible with the company's existing systems, including traditional local systems (such as LDAP) and cloud services (such as AWS, Microsoft 365), as well as different types of devices (such as Android, iOS devices, IoT devices, etc.) to avoid "compatibility blind spots.
Security and Compliance
Pay attention to the security measures of data during the integration process, such as whether encrypted transmission (TLS protocol, etc.) is used, whether sensitive data can be desensitized, and whether it complies with industry compliance standards (such as GDPR, medical industry data specifications, etc.).
Ease of use and operability
For non-technical personnel, are there simple and easy-to-use configuration tools (such as visual interfaces, templated configurations, etc.) to quickly complete basic integration settings and reduce dependence on professional developers?
Scalability and stability
Consider the future development needs of the enterprise, whether the solution can smoothly expand the scope of integration as the business grows, and whether it can maintain stable operation and avoid frequent failures when large-scale equipment or multiple systems are linked.
Unique Capabilities of AirDroid Business in MDM Integration
AirDroid Business, as a wholesome solution for your enterprise,, provides multi-system compatibility, open APIs, ease of use, and customizable integration capabilities. Here is what you can achieve with AirDroid Business as your MDM partner:
Customized consulting services to adapt to industry scenarios
Provide deeply customized integration consulting, covering deployment strategies (such as batch device migration, zero-touch deployment), product configuration (optimizing MDM functions for retail, medical, and other industry scenarios), and ecological cooperation (recommending adapted MSP service providers and hardware manufacturers).
For example, design remote equipment management processes for logistics companies, realize real-time troubleshooting of driver terminals through integrated scheduling systems, and reduce on-site operation and maintenance costs; provide medical institutions with equipment permission configuration solutions that meet compliance requirements to ensure the secure integration of medical terminals and electronic health record systems (EHR)."
Open up the partner ecosystem and expand the boundaries of integration
Build a diversified partner system, including dealers, resellers, MSP service providers, etc., and embed MDM capabilities into a wider range of enterprise systems through technical support and joint solution development.
For example, cooperate with IT service providers (MSP) to integrate AirDroid's remote control function into their operation and maintenance platform, so that customers can complete device monitoring and problem repair without switching systems; through OEM/ODM cooperation, provide hardware manufacturers with MDM module embedding solutions, so that devices have management capabilities when they leave the factory, shortening the enterprise deployment cycle."
Full-platform device support and efficient operation and maintenance integration
Supports cross-platform management of Android and Windows devices, and integrates with ITSM and monitoring systems through a unified API interface to achieve a closed loop of "monitoring - alarm - repair".
For example, a multinational company uses its API to synchronize the status data of thousands of retail terminals around the world to the SIEM platform. When an abnormality occurs on a device (such as excessive traffic or application crashes), AirDroid's remote repair instructions are automatically triggered, shortening the average problem resolution time by 70%."
Flexible scalability and cost control
Adapts to the integration needs of small and medium-sized enterprises to large groups, providing scalable pricing models and lightweight deployment options. For scenarios such as chain retail, asset data synchronization of thousands of devices and ERP systems can be quickly completed through pre-made templates; for start-ups, step-by-step integration is supported (such as first connecting to the HR system to realize automatic registration of employee devices, and then expanding to security monitoring), reducing initial investment costs."
4Challenges & Best Practices in MDM Integration
Let’s now discuss the most commonly faced challenges in achieving MDM integration and how to ensure a seamless integration process through best practices.
System Compatibility & Interface Hurdles
Challenges:
Different system interface standards and data formats are not unified (such as BAPI/XML for ERP and REST/JSON for MDM), resulting in docking failures.
Solutions:
Use middleware to convert non-standard interface formats and give priority to universal protocols (REST, SAML);
Use pre-made integration templates from mainstream systems to reduce custom development.
Verify compatibility through sandbox testing before integration."
Data Sync Delays/Inconsistencies
Challenges:
Data synchronization delays (such as delayed employee resignation information) or repeated pushes lead to invalid permission control and cost accounting errors.
Solutions:
Real-time data (such as resignation status) is synchronized using Webhooks, and non-real-time data (such as monthly statistics) is synchronized incrementally at regular intervals.
Set unique identifiers for key data, and perform regular two-way comparisons to verify consistency;
Cache data when the network is interrupted, and push it first after recovery."
Complex Permission Management
Challenges:
Policy conflicts caused by overlapping permissions of multiple systems, or permissions exceptions caused by missing configurations (e.g., compliant devices cannot access resources).
Solutions:
Clear permissions priority (e.g., security policies override business permissions), and visualize effective rules;
Let MDM permissions automatically inherit directory service user groups and synchronize changes.
Regularly audit permissions configuration, trigger alarms when exceptions occur, and support rollbacks."
Security & Compliance Risks
Challenges:
Unencrypted transmission, excessively open permissions leading to information leakage, or cross-border data transmission violating regulations (such as GDPR).
Solutions:
The entire link uses TLS 1.2 + encryption, sensitive fields are desensitized, and interfaces require OAuth/API Key authentication.
Localize core data according to regulatory requirements and use tools to detect cross-border transmission compliance;
Configure abnormal access rules, block connections when risks occur, and synchronize to SIEM."
Post-Integration O&M Complexity
Challenges:
The increase in the number of systems makes full-link monitoring difficult, and the scattered logs make fault location time-consuming (over 4 hours on average).
Solutions:
Use monitoring tools to integrate indicators (interface success rate, latency), set threshold alarms;
Add a unique tracking ID to synchronized data, and connect full-link logs to quickly locate faults;
Configure automated repair scripts for common problems."
Scalability Gaps Amid Changing Needs
Challenges:
When adjusting business (such as adding overseas branches), the rigidity of the integrated architecture leads to high secondary development costs.
Solutions:
Adopt a modular architecture, and only expand the corresponding modules when new requirements are added.
Support local/cloud/hybrid deployment, and adapt to cross-regional integration;
Reserve interface redundancy and use a low-code platform to quickly configure new rules."
5Conclusion
In short, MDM integration is essential for securing data, simplifying IT operations, and supporting remote work. With various integration styles to choose from, businesses should align their choice with their specific needs and resources. AirDroid Business is a reliable, all-in-one MDM solution offering flexible deployment, strong integration capabilities, and easy scalability, making it a smart choice for enterprises seeking efficient and secure device management.







Leave a Reply.