- What Is an Android Certificate & Why Should You Install It?
- Preparing to Install Certificates on Android
- Step-by-Step: How to Install Certificates on Android
- Installing Specific Types of Certificates
- Version & Brand-Specific Guides
- Managing Installed Certificates on Android
- Troubleshooting Common Certificate Installation Issues
- Why Choose AirDroid Business for Enterprise Certificate Management?
- FAQs
1 What Is an Android Certificate & Why Should You Install It?
Before delving into the details of how you can install Android certificates, let’s have a thorough understanding of what they are and how you should have them.
1What are Android Certificates?
An Android certificate is essentially a digital "credential of trust" issued by an authoritative organization (such as a CA, or Certificate Authority) or the enterprise itself. It's used to verify the legitimacy of a device, network, or application. It acts like a "digital contract" between a device and the network, ensuring the authenticity and security of information transmitted through encryption.
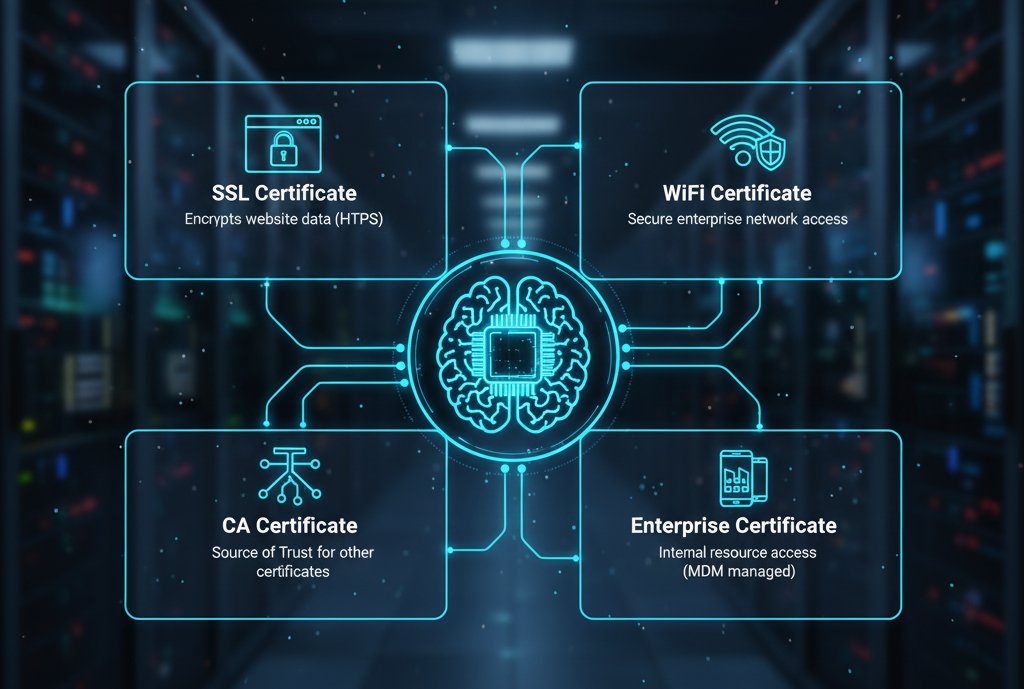
Common Android certificates include:
- SSL Certificate: Primarily used to encrypt data transmitted on HTTPS websites, preventing the theft of user information (such as usernames and passwords) entered in browsers or applications. It is essential for mobile devices to access secure websites.
- CA Certificate (Root Certificate): Issued by an authoritative CA organization, it serves as a "source of trust." Only when a device has a CA certificate installed will it recognize other certificates issued by that organization (such as SSL certificates). Otherwise, it may display a "certificate not trusted" message.
- WiFi Certificate: A dedicated identity credential for enterprise or public WiFi networks. It replaces traditional password authentication. Devices must have the corresponding certificate installed to access encrypted corporate WiFi networks, minimizing the risk of password leaks.
- Enterprise Certificate: Issued by the enterprise through the MDM (Mobile Device Management) system, it is used to verify whether employee devices have access to internal enterprise resources (such as VPNs, internal applications, email systems, etc.). It is a core tool for enterprise mobile security.
2Why are Certificates Essential for Your Android Device's Security?
Installing a certificate on an Android device essentially addresses the core issues of trust and security, with specific benefits in three areas:
- Ensuring Data Security: Certificates encrypt communications between devices and networks using cryptographic techniques (such as RSA and ECC). Even if data is intercepted, attackers cannot decipher the content. For example, SSL certificates ensure that payment information and account data are not leaked when users shop or log into banking apps on their Android phones.
- Enabling Accurate Authentication: Certificates serve as a device's "digital ID": Networks or applications verify the certificate on a device to confirm that the device is authorized to access. For example, a corporate WiFi certificate is tied to an employee's device's unique identifier (such as the IMEI). Only devices with the corresponding certificate can access the network, preventing unauthorized devices from "skimming" the network or stealing internal data.
- Meeting Compliance Requirements: Regulations (such as GDPR and HIPAA) in many industries (such as finance, healthcare, and education) explicitly require that enterprises implement strict authentication and data encryption for devices accessing sensitive data. Installing a compliance certificate is the basis for meeting these requirements - the issuance and use records of the certificate can be used as an audit basis to avoid penalties for "security non-compliance".
3Risks of Not Using Trusted Certificates on Android Devices
If an Android device doesn't have an installed or untrusted certificate, it may face a series of security and functional risks:
- Data Leakage and Hijacking: Without an SSL certificate, information accessing websites or apps may be transmitted in plain text, making it vulnerable to "man-in-the-middle" attacks, leading to account theft and privacy leaks (for example, using an unencrypted app on public WiFi).
- Inability to Access Restricted Resources: Corporate intranets, encrypted WiFi, VPNs, or internal applications typically only allow access from devices with designated certificates. If a device lacks a certificate, it will be blocked, impacting work efficiency (for example, employees cannot access the company's CRM system from their mobile phones).
- "Untrusted Certificate" Errors: If a device doesn't have the corresponding CA certificate installed, accessing HTTPS websites or using apps that rely on certificates will frequently result in "Invalid Certificate" prompts, or even inaccessible pages, impacting normal use.
- Loss of enterprise security defenses: For enterprises, devices without managed certificates can become security vulnerabilities. For example, if an employee uses a personal phone (without a corporate certificate installed) to access internal data, if the device is lost, attackers could bypass verification and steal sensitive information without the enterprise being able to track or intercept it.
By installing and managing trusted certificates, Android devices can strike a balance between "free use" and "security." This is especially true in enterprise scenarios. Using MDM tools (such as AirDroid Business) to deploy and manage certificates in bulk can further improve device security and management efficiency.
AirDroid Business - Mitigate Security Risks Efficiently
AirDroid Business MDM helps you mitigate security risks by ensuring all devices use trusted certificates. Prevent unauthorized access and safeguard sensitive information with our comprehensive MDM solution.
2 Preparing to Install Certificates on Android
1Downloading Your Certificate File (SSL, CA, WiFi Certificates)
Before starting the installation, the first step is to ensure you have the correct certificate files. These files typically come from your IT department, server administrator, or a Certificate Authority (CA). Be sure to obtain these files from a trusted source to ensure your device's security. You'll need to download different types of certificates depending on your goal:
- SSL/TLS certificates: If you need to access your company's internal websites or applications through a secure connection, your IT administrator will provide you with the corresponding SSL/TLS certificate files. These certificates are used to verify the server's identity and encrypt data transmission.
- CA certificate: In some enterprise environments, companies use a self-signed CA to issue internal certificates. In this case, you need to install the root certificate of the CA so that Android devices can trust all certificates issued by the CA.
- Wi-Fi Certificate: If your company's Wi-Fi network uses advanced security protocols like certificate-based EAP-TLS, you'll need to install a specific Wi-Fi certificate to successfully connect.
You can receive these files in a variety of ways, such as via email attachment, a link to your company's internal network drive, or by downloading them from a specific download link.
2Checking Certificate File Formats: Ensure Compatibility with Android Devices
Certificate files come in a variety of formats, and Android primarily supports a few. Verifying the file format before installation is crucial to avoiding installation failures.
The following are common certificate file formats compatible with Android devices:
- .cer, .crt, .pem: These are the most common certificate file extensions and typically represent the certificate itself. Most Android devices can directly recognize and install files in these formats.
- .p12 or .pfx: These file formats contain the certificate and its corresponding private key and are typically password-protected. In enterprise environments, the IT administrator will provide this file and the corresponding password. During installation, you will be prompted to enter this password to unlock the file.
If you receive a file format not listed above, or if you encounter an error message when attempting to install, we recommend contacting your IT department immediately to obtain the correct file or seek assistance. Avoid using unreliable tools to convert files on your own, as this can pose a security risk.
AirDroid Business - Simplify Certificate Deployment
With AirDroid Business MDM, automate the deployment of SSL, CA, and WiFi certificates. Save time and reduce errors with our easy-to-use platform.
3 Step-by-Step: How to Install Certificates on Android
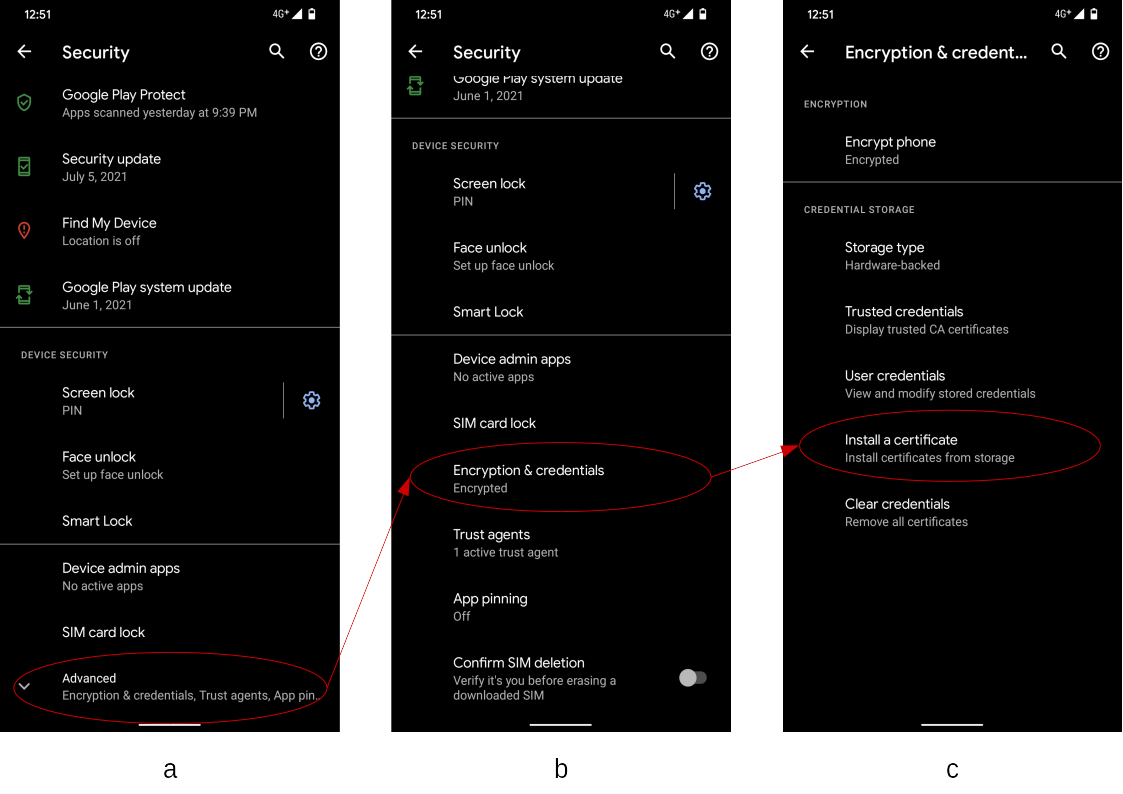
1General Method: Install Certificate on Android via Settings
This is the universal manual installation process for most Android devices. Even if your phone brand or operating system version is different, the core steps are generally similar.
- Step 1: Open Settings: Access your Android device's Settings menu.
- Step 2: Navigate to Security: In Settings, find and tap "Security & Privacy," "Biometrics & Security," or similar options.
- Step 3: Access Credential Management: In the Security settings, find "More Security Settings" or "Encryption & Credentials" and tap to access them.
- Step 4: Install the Certificate: On the Credential Management page, you'll see an option to "Install Certificate" or "Install Certificate from Storage." Tap it.
- Step 5: Select the Certificate File: This will open a file manager where you can select the downloaded certificate file. If the file is password-protected (such as .p12 or .pfx), you'll be prompted to enter the password.
- Step 6: Complete the Installation: After giving the certificate a name and confirming the name, the installation will complete.

2Install Android Certificate Using File Manager
If navigating through the settings is too tedious, you can try installing through a file manager, which is usually faster.
- Step 1: Open the file manager: Find and open the file manager app on your Android device.
- Step 2: Locate the certificate file: Navigate to the directory where you downloaded the certificate file (usually the Downloads folder).
- Step 3: Tap File: Find your certificate file (for example, mycert.crt or vpn.p12) and tap it.
- Step 4: Redirect to the installation screen: Android will automatically recognize this as a certificate file and redirect to the installation screen described in the "General method." Simply follow the prompts to complete the remaining steps.
3How to Add Certificate to Android for Enterprise Use (with MDM Tools like AirDroid Business)
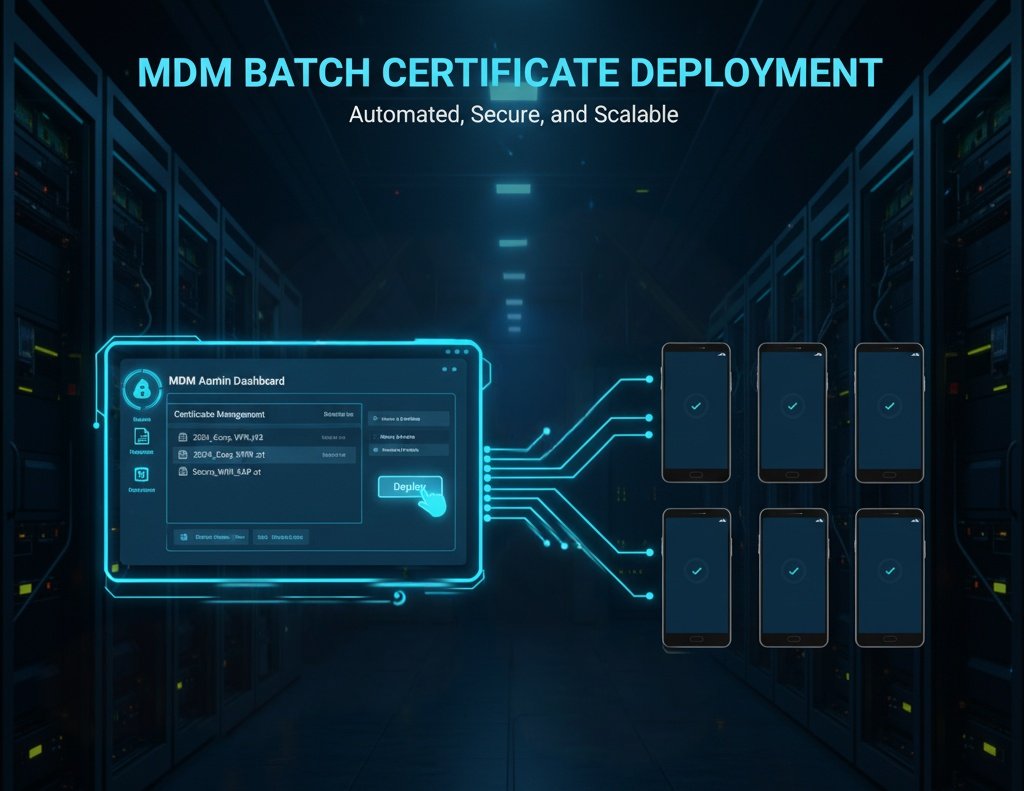
Enterprises need to install certificates on a large number of employee devices. Manual deployment is inefficient and prone to errors. Using MDM tools (such as AirDroid Business) allows for batch, automated deployment. The steps are as follows:
Administrator Operation (MDM Backend):
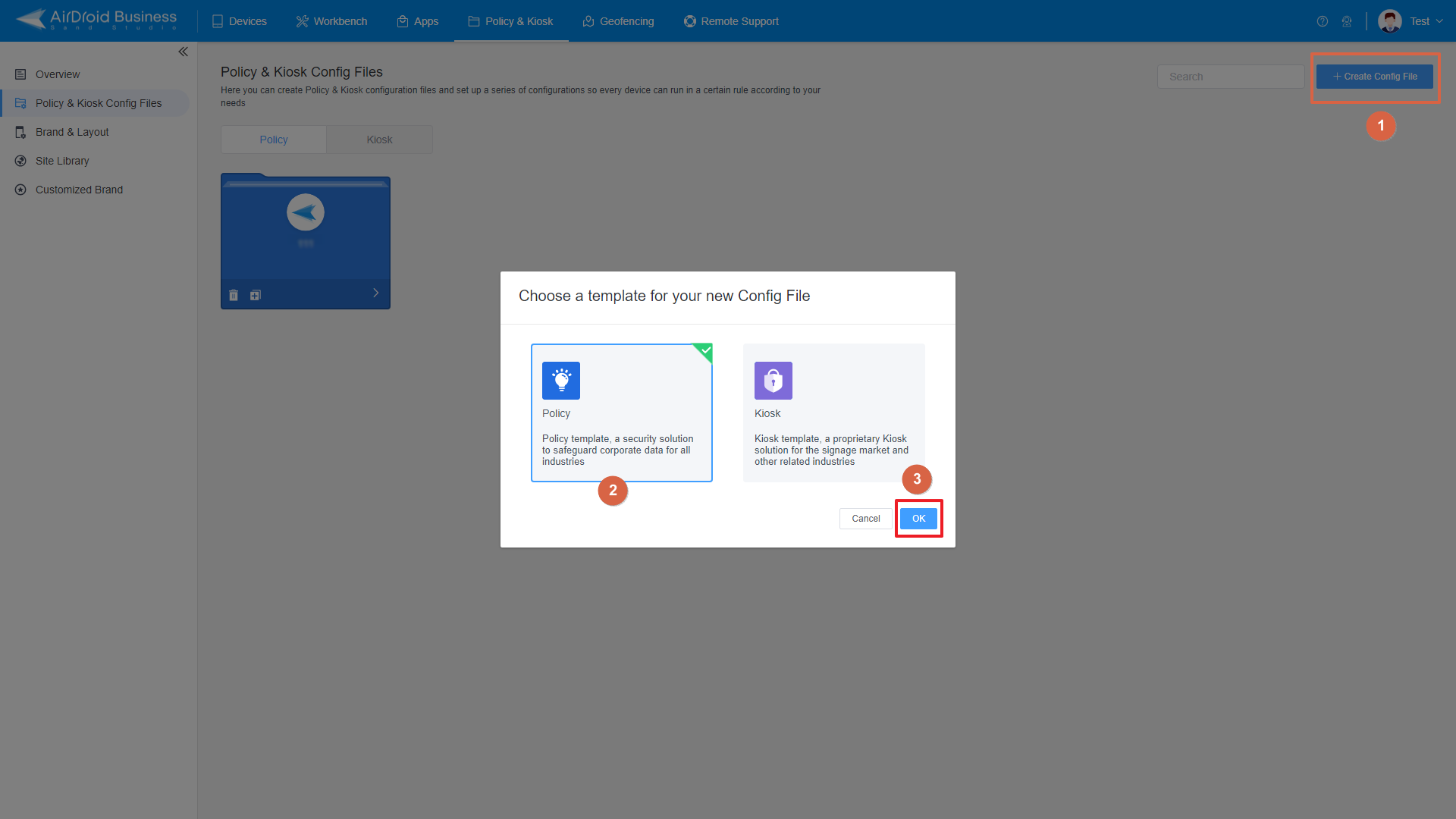
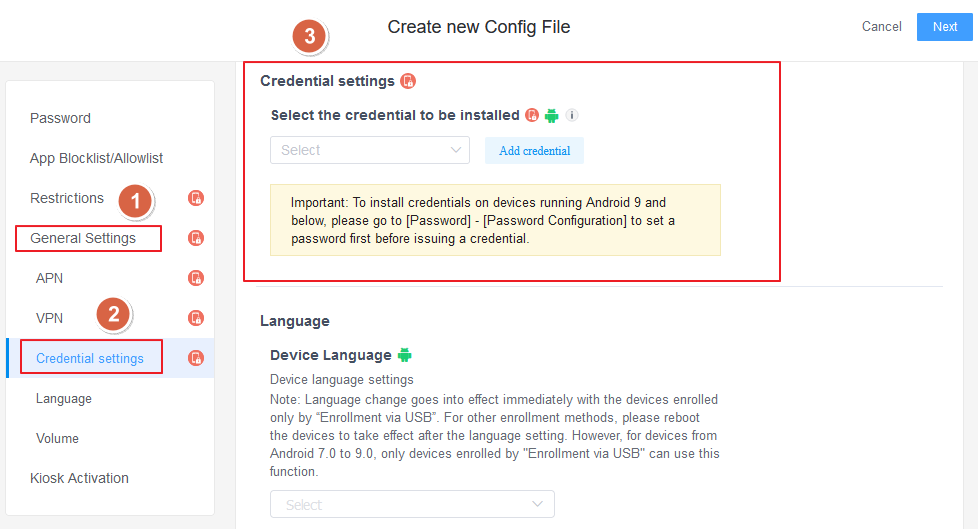
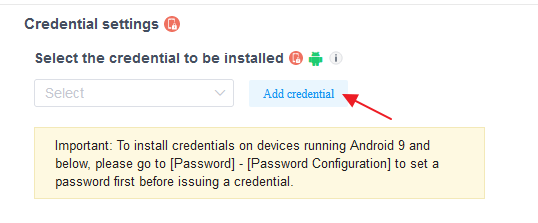
- Step 1: Upload the certificate to the MDM platform. Log in to the AirDroid Business admin backend → Go to "Policies & Profiles" → "Certificate Management" → Click "Add Certificate" to upload the enterprise certificate file (supports .crt/.pem/.p12 formats) and enter the certificate name and description (e.g., "2024 Enterprise WiFi Certificate").




- Step 2: Configure the deployment policy. Select target device groups: You can specify the deployment scope by department (e.g., "Sales Department," "Technology Department") or device type (e.g., company-issued devices/BYOD devices).


- Step 3: Click "Next" and confirm it.
Employee Device Experience:
- Step 1: No manual operation required: Once connected to the network, the device automatically receives the certificate and installs it (this operation occurs silently in the background, without disrupting employee work).
- Step 2: Automatic Permission Acquisition: The MDM tool has been granted enterprise device management permissions, eliminating the need for employees to manually grant "Install Certificate" permissions.
- Step 3: Transparency: Employees can view the certificate pushed by the company's MDM in "Settings" → "Security" → "Trusted Credentials" → "Enterprise" on their phones, ensuring device compliance.
Enterprise Benefits:
- Batch Efficiency: Certificates can be deployed to hundreds of devices in a single operation, eliminating manual installation time for each device (saving over 90%).
- Full Lifecycle Management: AirDroid Business automatically pushes updates to certificates before they expire. If an employee leaves or their device is lost, administrators can revoke the certificate with a single click, instantly cutting off the device's access to corporate resources.
- Secure and Controllable: Certificates are linked to the device's IMEI, preventing employees from privately exporting certificates to unauthorized devices and reducing the risk of leaks.
These three methods address the diverse needs of both individuals and businesses: Individual users can quickly install using Settings or a file manager; enterprise users can leverage MDM tools like AirDroid Business to ensure security while significantly improving management efficiency.
4 Installing Specific Types of Certificates
1How to Install SSL Certificate on Android
SSL certificates are primarily used to verify website identities and encrypt data. When installing an SSL certificate in your enterprise, select "VPN and Apps" for the certificate purpose at the end of the general installation process. This allows your devices to trust the certificate when accessing internal company websites and apps, ensuring a secure connection.
2Guide to Install CA Certificate on Android
CA certificates (Certification Authority certificates) are the foundation of the chain of trust. When installing a CA certificate, you may receive a warning that you're installing a non-publicly trusted CA. This is normal. If you're certain the certificate comes from a trusted company's IT department, you can ignore this warning and continue installation. Once a CA certificate is installed, your device will automatically trust all certificates issued by that CA.
3What Is a WiFi Install Certificate & How to Set It Up
Wi-Fi certificates are used to connect to enterprise Wi-Fi networks that use advanced security protocols (such as EAP-TLS). After installing the certificate, you'll need to complete the following configuration in Wi-Fi settings:
- Step 1: Select your enterprise network in the Wi-Fi list.
- Step 2: Under Authentication Method, select "TLS."
- Step 3: Under "CA Certificate" and "User Certificate," select the certificate you just installed.
- Step 4: Enter your identification information (such as your username or employee ID) as specified by your IT department and click Connect.
4Installing Enterprise Certificates for VPN/Internal Apps
Enterprise certificates (such as VPN certificates and internal app signing certificates) serve as "digital passes" for employees to access corporate resources. They must be integrated with the company's MDM system for batch control and security management. Their installation logic is completely different from that of personal certificates:
Core Features
- Certificates are bound to employee devices (via IMEI/serial number) to prevent unauthorized access.
- Admins can remotely manage (push, update, and revoke) certificates, eliminating manual employee operations.
- For use only with internal corporate resources (such as VPNs, OA systems, and internal CRM systems).
Installation Steps (using AirDroid Business as an example)
Administrator: Batch Deploy Certificates
- Step 1: Log in to the AirDroid Business admin dashboard and go to "Policies & Profiles" → "Certificate Management."
- Step 2: Upload the enterprise certificate (supports .crt/.p12 formats), enter the certificate name (e.g., "2024 VPN Certificate"), and the validity period.
- Step 3: Select the target device group (e.g., "Sales Department Phones"), set "Automatic Installation" and "Automatic Renewal 30 Days Before Expiration," and click "Deploy."
Employee-side: Automatic Receipt and Validation
- Step 1: Once connected to the internet, the device will silently receive the certificate (without pop-up notifications) and automatically install it.
- Step 2: When opening the enterprise VPN client or internal applications, the system automatically uses the installed certificate to complete authentication, eliminating the need for employees to enter a password.
Compared to manual installation by employees, managing certificates through MDM tools like AirDroid Business can reduce IT support costs by 90%, while also preventing risks like accidental certificate deletion and certificate leaks, ensuring secure and controllable access to corporate resources.
Installing different types of certificates is essentially a process of "scenario adaptation": individual users prioritize "quick validation," while enterprise users prioritize "security and control." Choosing the appropriate installation method based on the scenario ensures a balance of efficiency and security.
5 Version & Brand-Specific Guides
1Key Changes and Tips for Android 13/14 Certificate Installation
In Android 13 and later, Google has further strengthened its security policies. This makes certificate installation and trust management more stringent. Please pay special attention to the following points:
- Clearer purpose distinction: When installing a certificate, you will be asked to clearly specify the purpose of the certificate. Please choose the correct purpose between "VPN and Apps" and "Wi-Fi" based on your needs. If you select the incorrect purpose, the certificate may not be valid in the corresponding scenario.
- Enhanced security requirements: To ensure certificate security, Android 13 and later may require you to set a lock screen password for the certificate.
2Installation Guide for Samsung, Huawei, and Other Specific Devices
While the core process is similar, different phone brands customize the Android system, resulting in different certificate installation paths.
- Samsung devices: The certificate installation directory is typically located in Settings > Biometrics & security > More security settings.
- Huawei devices: You'll typically need to go to Settings > Security > More security settings, then find the installation option under Encryption & credentials.
- Xiaomi devices: You'll typically need to go to Settings > Passwords & security > System security, then find the "Install from storage" option under Encryption & credentials.
If you can't find the installation option using the above paths, the quickest way is to search for keywords like "certificate" or "credentials" in your phone's Settings to quickly locate it.
6 Managing Installed Certificates on Android
1Where Are the Certificates Stored on My Android Phone?
On Android devices, all installed certificates are stored in a centralized location for easy management and visibility. To find them, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Go to your phone's Settings.
- Step 2: Navigate to Security & Privacy (or a similar security option).
- Step 3: Find and tap Encryption & Credentials or More Security Settings.
- Step 4: Once there, you'll see an option for User Certificates. All certificates you've installed manually or pushed by your enterprise are stored here.
User Certificates are certificates installed by you or your enterprise.
System Certificates are certificates that come with Android and are used to trust major global certificate authorities.
2How to Update Expired Certificates on Android
Certificates typically have an expiration date. When a certificate expires, you need to replace it with a new one.
Manual Update: If you discover a certificate has expired, contact your IT administrator to obtain a new certificate file. Then, follow the installation steps in this guide to reinstall the new certificate. Android will automatically recognize and update the certificate.
MDM Tool Update: For enterprise IT administrators, AirDroid Business MDM provides efficient remote batch update functionality. Administrators can centrally manage certificates for all devices in the console. When a certificate is about to expire, they can push a new certificate to all devices in advance, eliminating the need for employees to manually update and ensuring uninterrupted business operations.
3Removing Unneeded Certificates from Android Devices
Removing a certificate may be necessary in some situations, such as when an employee leaves or a certificate is no longer trusted.
Manual Removal: Go to Settings > Security > Encryption & Credentials > User Certificates. Find the certificate you want to remove in the list, tap it to view its details, and then select "Remove" or "Delete."
Removal via MDM Tools: In enterprise environments, IT administrators can use AirDroid Business MDM to remotely revoke and remove certificates in bulk. This is crucial for ensuring enterprise data security and compliance.
7 Troubleshooting Common Certificate Installation Issues
1Certificate Not Installing on Android: Causes & Fixes
- Incorrect file format: Ensure the certificate file is in the correct format, such as .cer, .crt, or .p12.
- Password mismatch: If the certificate file requires a password (such as .p12), ensure the password is correct.
- Expired or incompatible certificate: Check the certificate's validity period and confirm that it is compatible with the device version.
2Ensuring Certificates Work with Enterprise MDM Solutions (e.g., AirDroid Business)
- Correct Deployment: Ensure the certificate was correctly deployed to the device via AirDroid Business. You can check the deployment history to confirm the status.
- Device Verification: Verify the certificate has been successfully installed in the device settings.
- Enterprise Policy: Ensure the device complies with the enterprise's security policy. If the certificate usage does not match, connection failures may occur.
8 Why Choose AirDroid Business for Enterprise Certificate Management?
1Bulk Certificate Deployment for Android Devices
In an enterprise environment, manually installing certificates for hundreds or even thousands of Android devices is a time-consuming and error-prone task. AirDroid Business MDM changes this reality. IT administrators simply upload the certificate file to a unified console and, with a single click, securely push the certificate to all designated Android devices or device groups. This remote, mass deployment method not only significantly saves time and labor but also eliminates human error and ensures consistent and accurate certificate deployment.
2Automated Certificate Lifecycle Management (Update, Revoke)
The core value of AirDroid Business MDM lies in its centralized visibility. Instead of checking individual devices individually, IT administrators can view certificate deployment status and expiration dates for all devices on a single console dashboard. Furthermore, administrators can use the "Deployment History" feature to track the success and failure of each certificate deployment, facilitating auditing and troubleshooting. This centralized management capability enables IT teams to proactively monitor certificate status, shifting from post-event firefighting to proactive review and ensuring enterprise network security.
3Enhanced Security with MDM-Integrated Certificate Trust
AirDroid Business MDM ensures all devices use trusted, enterprise-approved certificates, preventing employees from using unsafe certificates and enhancing overall security. The platform also supports remote certificate revocation. If a device is lost or stolen, or if an employee leaves the company, IT administrators can immediately remove the certificate from the device, severing access to corporate resources and effectively protecting sensitive data.
This integrated management approach ensures certificates are correctly configured and trusted on devices, fully integrating them with corporate security policies.
AirDroid Business - Experience Seamless Certificate Management
With AirDroid Business offers centralized management of your certificates, ensuring they are always up-to-date and secure. Enhance your enterprise's efficiency and security with our robust MDM solution.
FAQs
A certificate is a device's "digital credentials." Its core functions include:
- Encrypting data transmission (e.g., an SSL certificate protects HTTPS communications).
- Verifying device identity (e.g., a WiFi certificate allows access to an enterprise network).
- Ensuring access permissions (e.g., an enterprise certificate allows access to internal applications).
Simply put, certificates establish a "trusted connection" between a device and a network/application.
Yes, but this is subject to restrictions on the certificate type:
- Personal user certificates (such as SSL certificates and ordinary WiFi certificates) can be installed directly through Settings/File Manager without Root.
- CA certificates (system-level trusted) must be installed through MDM tools (such as AirDroid Business) on Android 7.0+ (no Root required, using enterprise permissions to bypass restrictions).
- Root is only required in special scenarios (such as installing system-level CA certificates on personal devices) and is not recommended (due to security risks).
Function-level: Access resources that rely on the certificate (such as connecting to corporate WiFi, opening internal apps). If they work normally without a "Certificate Error" prompt, it proves that the certificate is valid.
Enterprise scenario: Check "Certificate Deployment Status" in the AirDroid Business admin to intuitively see the installation results for each device.
There are risks, so exercise caution:
- Third-party certificates (such as those issued by non-authoritative organizations) may be embedded with malicious code, leading to "man-in-the-middle" attacks (data theft).
- Certificates with excessive permissions (such as system-level CA certificates) may be used to monitor device communications.
Recommendation: Only install certificates from trusted sources (such as corporate IT departments and well-known CAs). In enterprise scenarios, use MDM tools to centrally manage third-party certificates to prevent employees from installing them without authorization.









Leave a Reply.